Human lungs transfer oxygen fromair to blood due to cyclic inhaling and exhaling, but over time, the
Question:
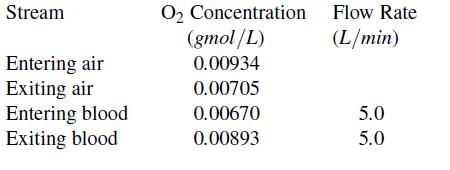
Human lungs transfer oxygen fromair to blood due to cyclic inhaling and exhaling, but over time, the process can be considered to be steady-state. As air enters the lungs, it contains a large amount of oxygen, and it then leaves the lungs with less oxygen.
Meanwhile, when blood enters the lungs, it contains less oxygen but leaves with more. The oxygen can be treated as a nonreacting species that merely transfers from the air to the blood. From the oxygen concentrations and the blood flow rates listed below, what flow rate of air must pass through the lungs (averaged over time)? The flow rate of air can be considered to be the same for the inspired (entering) air as for the expired (exiting) air.
Step by Step Answer:

Introduction To Chemical Engineering Tools For Today And Tomorrow
ISBN: 9780470885727
5th Edition
Authors: Kenneth A. Solen, John N. Harb





