An underground plastic pipe is to be used to carry water away from a building. As shown
Question:
An underground plastic pipe is to be used to carry water away from a building. As shown in Fig. P11.15, the pipe of diameter D will run downward and have both ends open to the air (pressure P0). The site requires a drop of H = 2 m over a length L = 40 m. The volume flow rate Q will depend on the weather, but it is supposed that it will not exceed 1 gal/s, or 3.8 × 10−3 m3/s (= Qmax). It is desired to choose an appropriate value for D.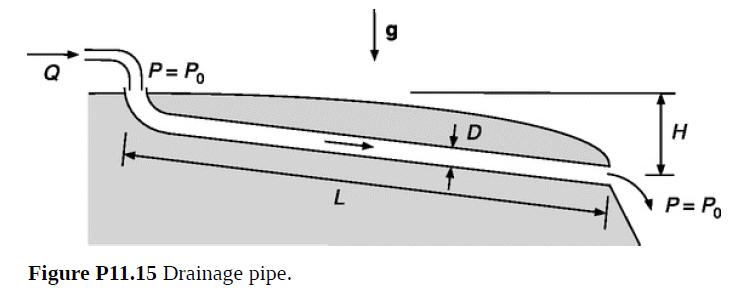
(a) Use the engineering Bernoulli equation to calculate the pipe diameter that will exactly accommodate the expected maximum flow. You may assume that the pipe is hydrodynamically smooth.
(b) If D is chosen as in part (a) and Q < Qmax, the pipe will not run full. How would you know that mathematically?
(c) For the same D, what would happen if ever Q > Qmax? Would the engineering Bernoulli equation still apply to the pipe?
Step by Step Answer:

Introduction To Chemical Engineering Fluid Mechanics
ISBN: 9781107123779
1st Edition
Authors: William M. Deen





