Continuing from the discussion in Problem 1, the subsequent step of the polymerization reaction is a reaction
Question:
Continuing from the discussion in Problem 1, the subsequent step of the polymerization reaction is a reaction of the product of the above step with more ethylene oxide.
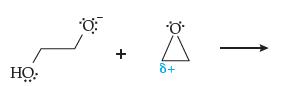
(a) Using the above mechanism and curved arrows, show what happens. How does this lead to the growth of the polymer chain?
(b) Addition of acid (H+) can halt the growth of the polymer. Explain how.
Data from Problem 1
An important industrial polymer is called polyethylene oxide (also called polyethylene glycol). It is made by adding a tiny amount of hydroxide ion (from NaOH) to ethylene oxide. They react via the following mechanism:
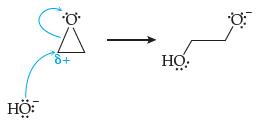
Why is the C in ethylene oxide labeled as δ+ (what is the justification for doing this)?
Why does the hydroxide ion “attack” the δ+ carbon atom?
The arrows show how electron pairs move. What is the fate of the hydroxide ion lone pair of electrons at the starting end of the blue arrow? What is the fate of the bonding electron pair in the C—O bond of ethylene oxide at the starting end of the blue arrow?
Where does the negative charge end up?
Step by Step Answer:

Introductory Chemistry Atoms First
ISBN: 9780321927118
5th Edition
Authors: Steve Russo And Michael Silver





