Consider the problem of prediciting the concentration of a reactant in an isothermal batch reactor, assuming a
Question:
Consider the problem of prediciting the concentration of a reactant in an isothermal batch reactor, assuming a first-order reaction, where the reaction rate, r, is given by the product of the reaction rate constant, k, and the concentration of the reactant, y:![dy dt y(0) = 1, = f(t, y) = r = -ky = y/t, t = [0, 10]. E](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1700/1/9/9/7546556fd4a36b331700199753708.jpg)
In this equation, we have introduced the time constant of the system, which is the inverse of the rate constant k, i.e. τ = 1/k. This simple problem involves a linear differential equation that allows us to investigate how the implicit and the explicit methods behave as the step size is modified. Recall that the explicit Euler method is given by yn+1 = yn + h f (xn, yn). This means that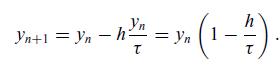
Therefore, if the time step, h, is larger than the time constant, the explicit method will predict negative concentrations and easily diverge, as shown in Figure 6.9(a). In contrast, the implicit Euler method yn+1 = yn + h f (xn+1, yn+1) has the advantage of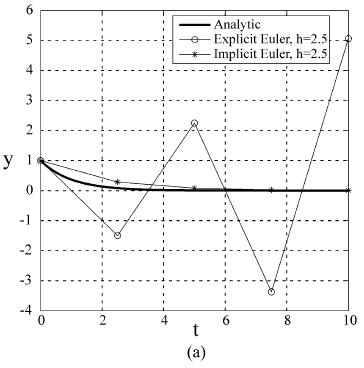
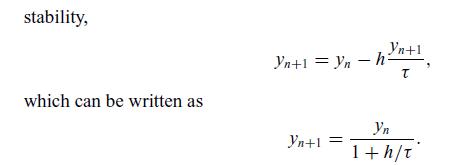
Step by Step Answer:

Mathematical Modeling In Chemical Engineering
ISBN: 9781107049697
1st Edition
Authors: Anders Rasmuson, Bengt Andersson, Louise Olsson, Ronnie Andersson





