The voltage across a capacitor is (V_{C}=q / C), where (C) is the capacitance and (q) is
Question:
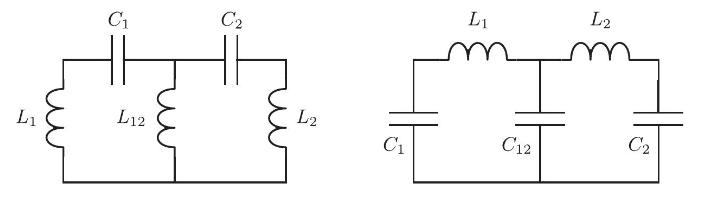
The voltage across a capacitor is \(V_{C}=q / C\), where \(C\) is the capacitance and \(q\) is the charge on the capacitor. The voltage across an inductor is \(V_{L}=L d I / d t\), where \(L\) is the inductance and \(I\) is the current through the inductor. A wire attached to a capacitor whose charge is changing carries a current \(I=d q / d t\). The net voltage drop around any closed circuit is zero, so a simple electrical \(L, C\) circuit obeys \(L \ddot{q}+q / C=0\), and so oscillates with frequency \(\omega=1 / \sqrt{L C}\). Find the normal mode oscillation frequencies and eigenvectors for each of the two-loop circuits shown, in the case \(C_{1}=C_{2} \equiv C, L_{1}=L_{2} \equiv L, C_{12}=2 C\), and \(L_{12}=2 L\).
Fantastic news! We've Found the answer you've been seeking!
Step by Step Answer:
Related Book For 

Question Posted:





