The system has a steady state at (x 1 = 1, x 2 = 1). You can
Question:
The system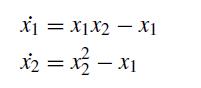
has a steady state at (x1 = 1, x2 = 1). You can analyze this steady state using linear stability analysis, or just consider the phase plane in Fig. 5.23. What can you say about the real and imaginary parts of the eigenvalues of the steady state Jacobian for this problem? You can provide a qualitative answer based on the phase plane or a numerical value based on linear stability analysis, whichever you prefer.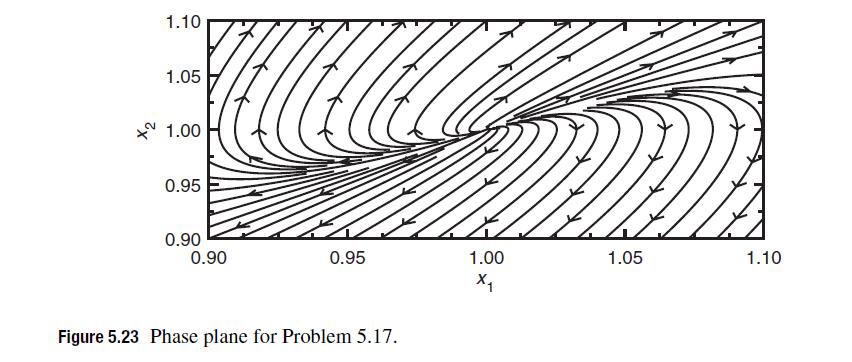
Fantastic news! We've Found the answer you've been seeking!
Step by Step Answer:
Related Book For 

Numerical Methods With Chemical Engineering Applications
ISBN: 9781107135116
1st Edition
Authors: Kevin D. Dorfman, Prodromos Daoutidis
Question Posted:





