The reducing agent in the double-bond reduction step of fatty-acid biosynthesis (the last step of Eq. 22.74,
Question:
The reducing agent in the double-bond reduction step of fatty-acid biosynthesis (the last step of Eq. 22.74, repeated below) is NADPH. (ACP 5 acyl carrier protein.)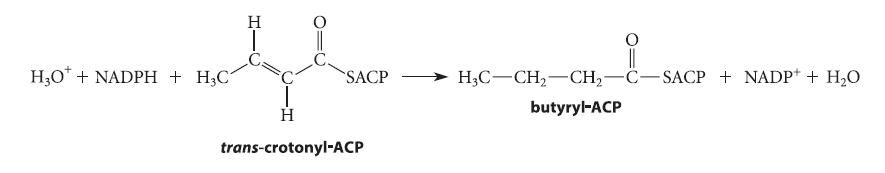
(a) Using an abbreviated structure for NADPH, and assuming that acids and bases are available as needed in the enzyme active site, draw a curved-arrow mechanism for this reaction.
(b) Explain why this reaction is an example of a conjugate addition.
(c) When NADPD (a deuterium-labeled NADPH, below) and D2O are used in the enzyme-catalyzed reduction of transcrotonyl-ACP, the product is the (2S,3R) stereoisomer of the doubly deuterated butyryl-ACP. Is this conjugate-addition reaction a syn- or an anti-addition? Give your reasoning.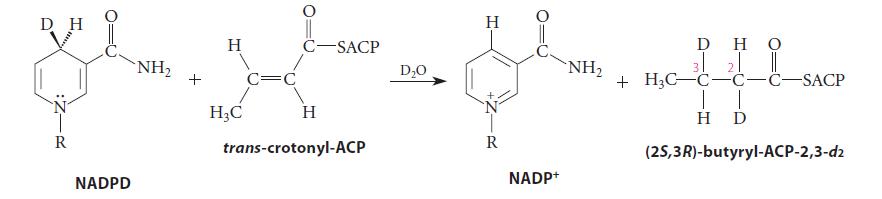
Fantastic news! We've Found the answer you've been seeking!
Step by Step Answer:
Related Book For 

Question Posted:





