Suppose a cell is taking water into two vacuoles. Let V 1 denote the volume of the
Question:
Suppose a cell is taking water into two vacuoles. Let V1 denote the volume of the first vacuole and V2 the volume of the second. In each of the following cases,
a. Solve the given differential equations for V1(t) and V2(t).
b. Write a differential equation for V = V1 + V2, including the initial condition.
c. Show that the solution of the differential equation for V is the sum of the solutions for V1 and V2.
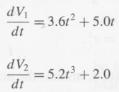
with initial conditions V1(0) = 5.0 μm3 and V2(0) = 10.0 μm3.
Fantastic news! We've Found the answer you've been seeking!
Step by Step Answer:
Related Book For 

Modeling the Dynamics of Life Calculus and Probability for Life Scientists
ISBN: 978-0840064189
3rd edition
Authors: Frederick R. Adler
Question Posted:





