The molar integral heat of solution s H is defined as the change in enthalpy that
Question:
The molar integral heat of solution ΔsH is defined as the change in enthalpy that results when 1 mole of solute (component 1) is isothermally mixed with N2 moles of solvent (component 2) and is given by
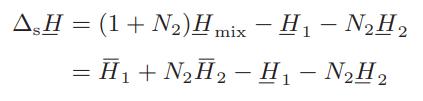
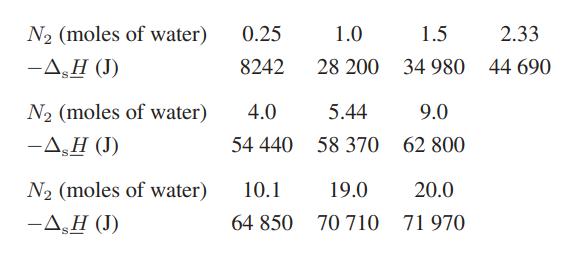
ΔsH is easily measured in an isothermal calorimeter by monitoring the heat evolved or absorbed on successive additions of solvent to a given amount of solute. The table below gives the integral heat-ofsolution data for 1 mol of sulfuric acid in water at 25°C (the negative sign indicates that heat is evolved in the dilution process).
a. Calculate the heat evolved when 100 g of pure sulfuric acid is added isothermally to 100 g of water.
b. Calculate the heat evolved when the solution prepared in part (a) is diluted with an additional 100 g of water.
c. Calculate the heat evolved when 100 g of a 60 wt % solution of sulfuric acid is mixed with 75 g of a 25 wt % sulfuric acid solution.
d. Relate (H1 − H1) and (H2 − H2) to only N1, N2, ΔHs, and the derivatives of ΔHs with respect to the ratio N2/N1.
e. Compute the numerical values of (H1 − H1) and (H2 − H2) in a 50 wt % sulfuric acid solution.
Step by Step Answer:

Chemical Biochemical And Engineering Thermodynamics
ISBN: 9780470504796
5th Edition
Authors: Stanley I. Sandler