Consider the reaction of methanol to dimethyl ether (DME) via the gas-phase catalytic reaction using an amorphous
Question:
Consider the reaction of methanol to dimethyl ether (DME) via the gas-phase catalytic reaction using an amorphous alumina catalyst treated with 10.2% silica.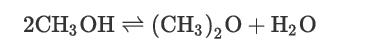
There are no significant side reactions at temperatures less than 400°C, and the equilibrium conversion at these temperatures is greater than 99%. At temperatures greater than 250°C, the rate equation is given by Bondiera and Naccache [2] as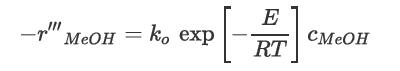
where ![]() is the rate of reaction of methanol inmol/m catalyst/s, k = 3.475 × 106 m3 reactor/m3 catalyst/s, E = 84.06 kJ/mol3, and cMeOH = concentration of methanol in mol/m3 reactor. A typical feed to a packed bed reactor is 98% methanol at a pressure of approximately 14 atm. This reaction is exothermic and the temperature is expected to rise from 250°C to 350°C across the reactor bed with an expected conversion of methanol across the reactor of 80%.
is the rate of reaction of methanol inmol/m catalyst/s, k = 3.475 × 106 m3 reactor/m3 catalyst/s, E = 84.06 kJ/mol3, and cMeOH = concentration of methanol in mol/m3 reactor. A typical feed to a packed bed reactor is 98% methanol at a pressure of approximately 14 atm. This reaction is exothermic and the temperature is expected to rise from 250°C to 350°C across the reactor bed with an expected conversion of methanol across the reactor of 80%.
For this system, determine if there are any pore diffusion effects at the
1. Reactor inlet
2. Reactor outlet
3. For Part (b) determine the overall effectiveness including external mass transfer, and comment on the influence of external mass transfer to the overall reaction rate.
The internal diffusion coefficient for the porous catalyst is estimated to be 8 × 10-8 m2/s, and the minimum catalyst particle size to avoid excessive pressure drop is estimated to be 3 mm diameter spheres. The mass transfer coefficient for methanol at 350°C and 14 atm pressure for this size of catalyst is approximately km = 2.41 × 10-3 m/s.
Step by Step Answer:

Analysis Synthesis And Design Of Chemical Processes
ISBN: 9780134177403
5th Edition
Authors: Richard Turton, Joseph Shaeiwitz, Debangsu Bhattacharyya, Wallace Whiting





