Question: a) b) c) d) e) f) The two N-channel MOSFETS in Figure A1 operate in saturation region and their bulk terminals are connected to
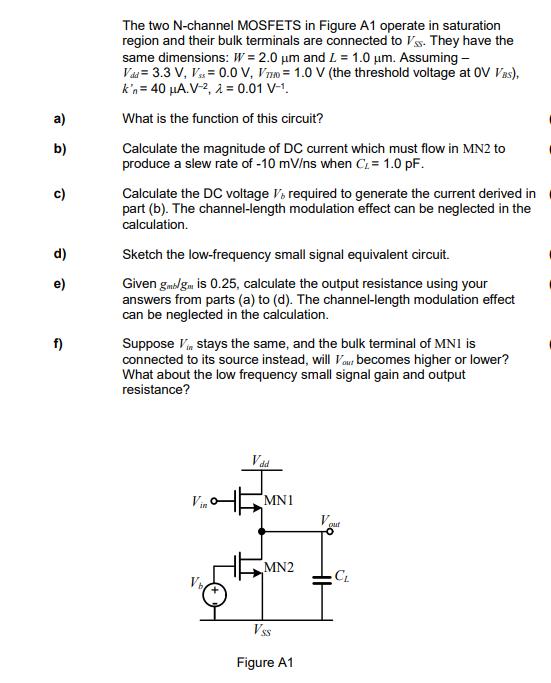
a) b) c) d) e) f) The two N-channel MOSFETS in Figure A1 operate in saturation region and their bulk terminals are connected to Vs. They have the same dimensions: W= 2.0 m and L = 1.0 m. Assuming - Vad = 3.3 V, Vs = 0.0 V, V = 1.0 V (the threshold voltage at OV VBS), k'n = 40 A.V-2, = 0.01 V-. What is the function of this circuit? Calculate the magnitude of DC current which must flow in MN2 to produce a slew rate of -10 mV/ns when C = 1.0 pF. Calculate the DC voltage V, required to generate the current derived in part (b). The channel-length modulation effect can be neglected in the calculation. Sketch the low-frequency small signal equivalent circuit. Given gmb/gm is 0.25, calculate the output resistance using your answers from parts (a) to (d). The channel-length modulation effect can be neglected in the calculation. Suppose V stays the same, and the bulk terminal of MNI is connected to its source instead, will you becomes higher or lower? What about the low frequency small signal gain and output resistance? Vin V Vdd MN1 MN2 Vss Figure A1 out CL
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
a This circuit is a commonsource amplifier with resistive load MN1 acts as the input transistor and ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


