Question: _______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ Signal.h: #include #include #include using namespace std; class Signal { private: vector m_samples; public: Signal() { m_samples.clear(); } Signal(const vector& smp) : m_samples{smp} {


_______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Signal.h:
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
class Signal {
private:
vector m_samples;
public:
Signal() {
m_samples.clear();
}
Signal(const vector& smp) :
m_samples{smp} {
}
Signal(const Signal& sig) :
m_samples{sig.m_samples} {
}
~Signal() {
m_samples.clear();
}
unsigned int length() const {
return m_samples.size();
}
int min() const;
int max() const;
double avg() const;
int energy() const;
double mse(const Signal& sig) const; // Mean Squared Error
Signal downSample(int factor);
Signal operator+(int offset); // ex: sig + 2
Signal operator+(const Signal& sig); // ex: sig1 + sig2
Signal operator*(int scale); // ex: sig * 2
Signal operator*(const Signal& sig); // ex: sig1 * sig2
Signal operator>>(unsigned int shift); // ex: sig >> 2
Signal operator
int operator[](int index) const;
friend ifstream& operator>>(ifstream& ifs, Signal& sig); // ex: ifs >> sig
};
Signal operator+(int offset, const Signal& sig); // ex: 3 + sig
Signal operator*(int scale, const Signal& sig); // ex: 3 * sig
ostream& operator
ofstream& operator
_______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Signal.cpp:
#include
#include
#include "Signal.h"
int Signal::min() const {
int min = m_samples[0];
for (int i = 1; i
if (min > m_samples[i]) {
min = m_samples[i];
}
}
return min;
}
int Signal::max() const {
// Fill in function defn
return 0;
}
double Signal::avg() const {
double avg = 0;
for (int i = 0; i
avg += m_samples[i];
}
return avg / length();
}
int Signal::energy() const {
int enr = 0;
for (int i = 0; i
enr += m_samples[i] * m_samples[i];
}
return enr;
}
double Signal::mse(const Signal& sig) const {
int size = (length() > sig.length()) ? length() : sig.length();
double pwr = 0;
for (int i = 0; i
double err = operator[](i) - sig[i];
pwr += err * err;
}
return pwr / size;
}
Signal Signal::downSample(int factor) {
vector tmp;
for (int i = 0; i
tmp.push_back(m_samples[i]);
}
m_samples = tmp;
return Signal(m_samples);
}
Signal Signal::operator+(int offset) {
vector tmp;
for (int i = 0; i
tmp.push_back(m_samples[i] + offset);
}
return Signal(tmp);
}
Signal Signal::operator+(const Signal& sig) {
int size = (length() > sig.length()) ? length() : sig.length();
vector tmp;
for (int i = 0; i
tmp.push_back(operator[](i) + sig[i]);
}
return Signal(tmp);
}
Signal Signal::operator*(int scale) {
// Fill in function defn
Signal sig;
return sig;
}
Signal Signal::operator*(const Signal& sig) {
vector tmp(length() + sig.length() - 1, 0);
for (int i = 0; i
for (int j = 0; j
tmp[i] += m_samples[j] * sig[i - j];
}
}
return Signal(tmp);
}
Signal Signal::operator>>(unsigned int shift) {
vector tmp;
for (int i = 0; i
tmp.push_back(0);
}
for (int i = 0; i
tmp.push_back(m_samples[i]);
}
m_samples = tmp;
return Signal(m_samples);
}
Signal Signal::operator
vector tmp;
for (int i = shift; i
tmp.push_back(m_samples[i]);
}
m_samples = tmp;
return Signal(m_samples);
}
int Signal::operator[](int index) const {
if (index = length()) {
return 0;
}
return m_samples[index];
}
Signal operator+(int offset, const Signal& sig) {
vector tmp;
for (int i = 0; i
tmp.push_back(sig[i] + offset);
}
return Signal(tmp);
}
Signal operator*(int scale, const Signal& sig) {
vector tmp;
for (int i = 0; i
tmp.push_back(sig[i] * scale);
}
return Signal(tmp);
}
ifstream& operator>>(ifstream& ifs, Signal& sig) {
sig.m_samples.clear();
string str1, str2;
ifs >> str1 >> str2;
while (true) {
int idx = 0, smp = 0;
ifs >> idx >> smp;
if (ifs.eof()) {
break;
}
sig.m_samples.push_back(smp);
}
return ifs;
}
ostream& operator
os
for (int i = 0; i
os
}
return os;
}
ofstream& operator
ofs
for (int i = 0; i
ofs
}
return ofs;
}
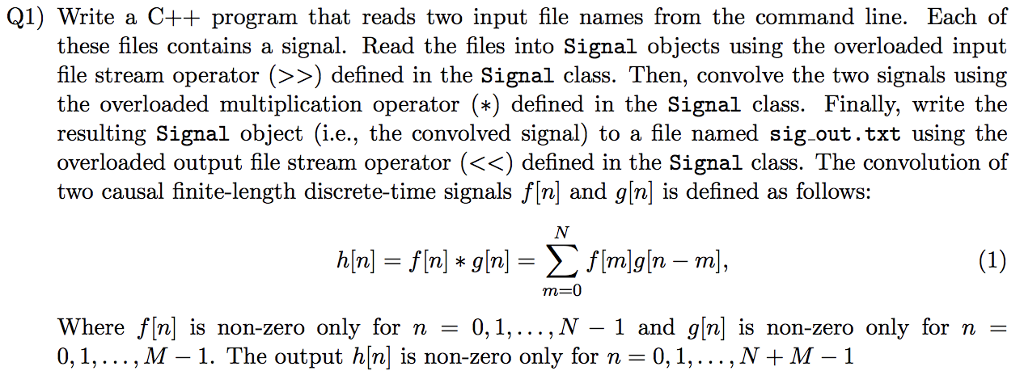
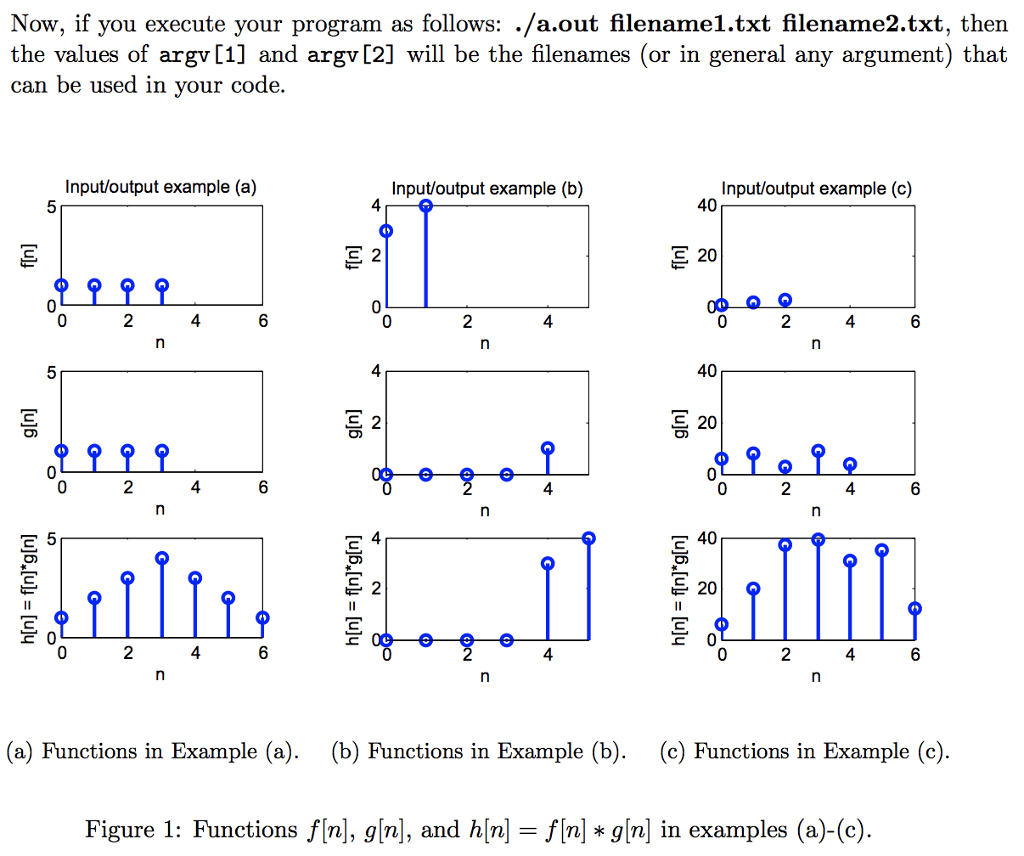
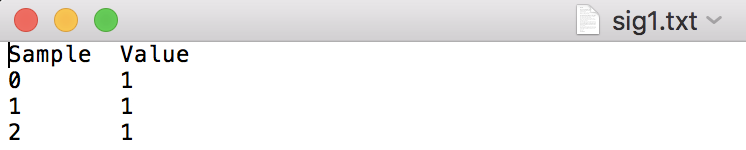
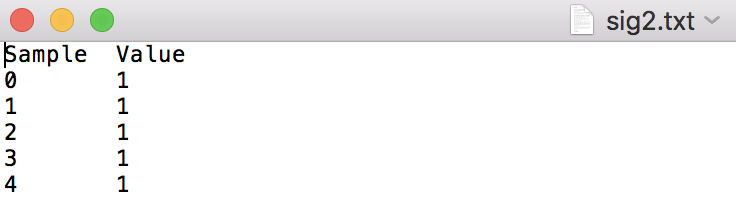
Q1) Write a C++ program that reads two input file names from the command line. Each of these files contains a signal. Read the files into Signal objects using the overloaded input file stream operator (>>) defined in the Signal class. Then, convolve the two signals using the overloaded multiplication operator (*) defined in the Signal class. Finally, write the resulting Signal object (i.e., the convolved signal) to a file named sig-out.txt using the overloaded output file stream operator (Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


