Study this transition in terms of graphs of typical solutions (Cf. Fig. 46)(a) Avoiding unnecessary generality is
Question:
Study this transition in terms of graphs of typical solutions (Cf. Fig. 46)(a) Avoiding unnecessary generality is part of good modeling. Decide that the initial value problems (A) and (B).(A) y" + cy' + y = 0, y(0) = 1, y'(0) = 0(B) The same with different c and y' (0) = ?? 2 (instead of 0), will give practically as much information as a problem with other m, k, y(0), y' (0).(b) Consider (A), Choose suitable values of c, perhaps better ones than in Fig. 46 for the transition from Case III to II and I. Guess c for the curves in the figure.(c) Time to go to rest. Theoretically, this time is infinite (why?) Practically, the system is at rest when its motion has become very small, say, less than 0.1 % of the initial displacement (this choice being up to us), that is in our case, (11) |y(t)| (d) Solve (A) analytically, give a reason why the solution c of y(t2) = ?? 0.001, with t1 the solution of y'(t) = 0, will give you the best possible c satisfying (11).(e) Consider (B) empirically as in (a) and (b) what is the main difference between (B) and(A)?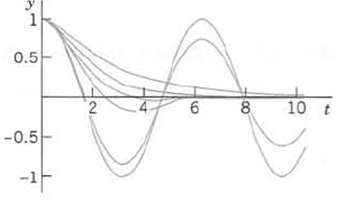
Step by Step Answer:

A First Course in Differential Equations with Modeling Applications
ISBN: 978-1305965720
11th edition
Authors: Dennis G. Zill





