Question: An electronic device is cooled by passing air at 27?C through six small tubular passages in parallel drilled through the bottom of the device as
An electronic device is cooled by passing air at 27?C through six small tubular passages in parallel drilled through the bottom of the device as shown below. The mass flow rate per tube is 7 x 10??5 kg/s.Heat is generated in the device resulting in approximately uniform heat flux to the air in the cooling passage. To determine the heat flux, the air outlet temperature is measured and found to be 77?C. Calculate the rate of heat generation, the average heat transfer coefficient, and the surface temperature of the cooling channel at the center and at the outlet.GIVENAir flow through small tubular passages as shown aboveAir temperatureEntrance (Tb,in) = 27?CExit (Tb,out) = 77?CMass flow rate per passage (m)= 7 x 10??5 kg/sNumber of passages (N) = 6ASSUMPTIONSSteady stateUniform heat generationUniform heat flux to the airViscosity variation is negligibleHeat transfer coefficient is approximately constantaxially
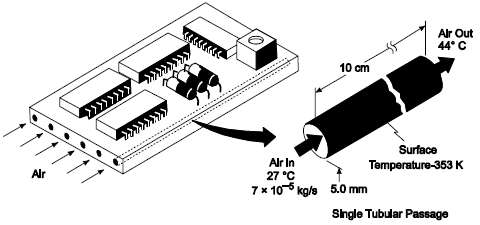
Alr Out 44 C 10 cm >>>> Surface Alr In 27 C Temperature-353 K Alr 7x 105 kg/e 5.0 mm Single Tubular Passage
Step by Step Solution
3.53 Rating (170 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
The Reynolds number is The thermal entrance length is given by Equation 68 ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Document Format (1 attachment)
66-E-M-E-H-M-T (1742).docx
120 KBs Word File


