Question: An ideal analog integrator is described by the system function H a (s) = 1/s. A digital integrator with system function H(z) can obtained by
An ideal analog integrator is described by the system function Ha(s) = 1/s. A digital integrator with system function H(z) can obtained by use of the bilinear transformation. That is,
(a) Write the difference equation for the digital integrator relating the input x(n) to the output y(n).
(b) Roughly sketch the magnitude |Ha(j?)| and phase ?(?) of the analog integrator.
(c) It is easily verified that the frequency response of the digital integrator is roughly sketch |H(?)| and ?(?).
(d) Compare the magnitude and phase characteristics obtained in parts (b) and (c). How well does the digital integrator match the magnitude and phase characteristics of the analog integrator?
(e) The digital integrator has a pole at z = 1. If you implement this filter on a digital computer, what restrictions might you place on the input single sequence x(n) to avoid computational difficulties?
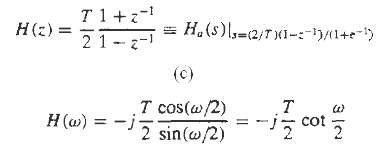
T 1+z- 21 - z- (c) T cos(w/2) 2 sin(@/2) H(2) = = H,(s),-2T)1-:-)(1+e-) -z cot H (a) = - 2
Step by Step Solution
3.39 Rating (168 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Let T 2 a Hz 1 z 1 1 z 1 yn yn 1 xn xn 1 b c d The digital integrator ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Document Format (1 attachment)
31-E-T-E-D-S-P (878).docx
120 KBs Word File


