Question: Consider a 5-mm-square, diffuse surface ?Ao having a total emissive power of Eo = 4000 W/m2. The radiation field due to emission into the hemispherical
Consider a 5-mm-square, diffuse surface ?Ao having a total emissive power of Eo = 4000 W/m2. The radiation field due to emission into the hemispherical space above the surface is diffuse, thereby providing a uniform intensity I (?, ?). Moreover, if the space is a non-participating medium (non-absorbing, non-scattering, and non-emitting), the intensity is independent of radius for any (?, ?) direction. Hence intensities at any points P1 and P2 would be equal.
(a) What is the rate at which radiant energy is emitted by ?Ao, qemit?
(b) What is the intensity Io,e of the radiation field emitted from the surface ?Ao?
(c) Beginning with Equation 12.8 and presuming knowledge of the intensity Io.e, obtain an expression for qemit.
(d) Consider the hemispherical surface located at r = R1 = 0.5 m. Using the conservation of energy requirement, determine the rate at which radiant energy is incident on this surface due to emission from ?Ao.
(e) Using Equation 12.6, determine the rate at which radiant energy leaving ?Ao is intercepted by the small area ?A2 located in the direction (45°, ?) on the hemispherical surface. What is the irradiation on ?A2?
(f) Repeat part (e) for the location (0°, ?). Are the irradiations at the two locations equal?
(g) Using Equation 12.13, determine the irradiation G1 on the hemispherical surface at r = R1.
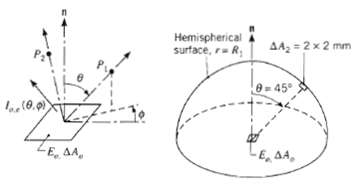
Hemispherical surface, r R; AA, = 2 x 2 mm 8-45 (0.0) E. , -E, A,
Step by Step Solution
3.33 Rating (174 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
KNOWN Diffuse surface AA 5mm square with total emissive power E 4000 Wm FIND a Rate at which radiant energy is emitted by AA qemit b Intensity L of the radiation field emitted from the surface AA c Ex... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Document Format (1 attachment)
8-E-M-E-H-M-T (1094).docx
120 KBs Word File


