Question: Determine the heat transfer coefficient at the stagnation point and the average value of the heat transfer coefficient for a single 5-cm-OD, 60-cm-long tube in
Determine the heat transfer coefficient at the stagnation point and the average value of the heat transfer coefficient for a single 5-cm-OD, 60-cm-long tube in cross-flow. The temperature of the tube surface is 260?C, the velocity of the fluid flowing perpendicularly to the tube axis is 6 m/s, and its temperature is 38?C. The following fluids are to be considered(a) Air,(b) Hydrogen, and(c) Water.GIVENA single tube in cross-flowTube outside diameter (D) = 5 cm = 0.05 mTube length (L) = 60 cm = 0.6 cmTube surface temperature (Ts) = 260?CFluid velocity (V) = 6 m/sFluid temperature (Tb) = 38?CASSUMPTIONSSteady stateTurbulence level of the free stream approaching the tube islow
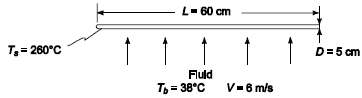
L- 60 cm D=5 cm T= 260C Fluld T = 38C V-6m/s
Step by Step Solution
3.39 Rating (168 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
For air as the fluid The Reynolds number is The heat transfer coeffi... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Document Format (1 attachment)
66-E-M-E-H-M-T (1784).docx
120 KBs Word File


