Question: Environmental concerns have recently motivated the search for replacements for chlorofluorocarbon refrigerants. An experiment has been devised to determine the feasibility of such a replacement.
Environmental concerns have recently motivated the search for replacements for chlorofluorocarbon refrigerants. An experiment has been devised to determine the feasibility of such a replacement. A silicon chip is bonded to the bottom of a thin copper plate as shown in the sketch below. The chip is 0.2 cm thick and has a thermal conductivity of 125 W/(m K). The copper plate is 0.1 cm thick and there is no contact resistance between the chip and the copper plate. This assembly is to be cooled by boiling a saturated liquid refrigerant on the copper surface. The electronic circuit on the bottom of the chip generates heat uniformly at a flux of q'' = 5 x 104 W/m2. Assume that the sides and the bottom of the chip are insulated. Calculate the steady state temperature at the copper surface and the bottom of the chip, as well as the maximum heat flux in pool boiling, assuming that the boiling coefficient, Csf, is the same as for n-pentane on lapped copper. The physical properties of this new coolant are: Tsat = 60?C, cp = 1100 J/(kg K), hfg = 8.4 x 104 J/kg, ρl = 1620 kg/m3, ρv = 13.4 kg/m3, σ = 0.081 N/m, μl = 4.4 x 10??4 kg/(ms) and Prl = 9.0.GIVENA new refrigerant boiling on top of a copper plate, cooling a silicon chipThe refrigerant is a saturated liquidProperties of the refrigerant and CsfNo contact resistance between the copper plate and the chipUniform heat flux produced by the chip is 5 x 104W/m2
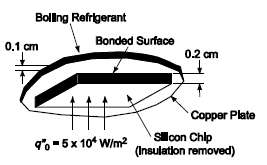
Bollng Refrigerant Bonded Surface 0.1 cm 0.2 cm Copper Plate Slcon Chlp (Insulation removed) go-5x 10 W/m?
Step by Step Solution
3.37 Rating (163 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
The right side of the sketch above shows the thermal circuit The heat generated at the bottom of the ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Document Format (1 attachment)
66-E-M-E-H-M-T (1950).docx
120 KBs Word File


