Question: For a rotating disk electrode operating at sufficiently great potential, the redox reaction rate is governed by the rate at which analyte diffuses through the
For a rotating disk electrode operating at sufficiently great potential, the redox reaction rate is governed by the rate at which analyte diffuses through the diffusion layer to the electrode. The thickness of the diffusion layer is
![]() where D is the diffusion coefficient of reactant (m2/s), is the kinematic viscosity of the liquid (= viscosity/density = m2/s), and ω is the rotation rate (radians/s) of the electrode. There are 2π radians in a circle. The current density (A/m2) is
where D is the diffusion coefficient of reactant (m2/s), is the kinematic viscosity of the liquid (= viscosity/density = m2/s), and ω is the rotation rate (radians/s) of the electrode. There are 2π radians in a circle. The current density (A/m2) is
![]()
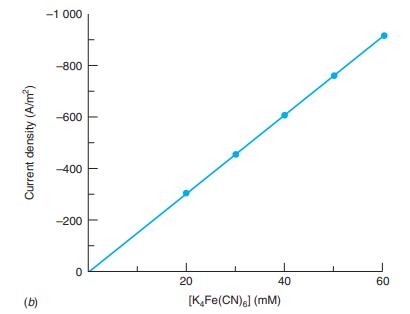
where n is the number of electrons in the half-reaction, F is the Faraday constant, and C0 is the concentration of the electroactive species in bulk solution (mol/m3 , not mol/L). Consider the oxidation of Fe(CN)64- in a solution of 10.0 mM K3Fe(CN)6 = 50.0 mM K4Fe(CN)6 at = 0.90 V (versus S.C.E.) at a rotation speed of 2.00 ×103 revolutions per minute.20 The diffusion coefficient of Fe(CN)64- is 2.5 × 10-9 m2/s, and the kinematic viscosity is 1.1 x 106 m2/s. Calculate the thickness of the diffusion layer and the current density. If you are careful, the current density should look like the value in Figure 16-14b.
Figure 16-13b
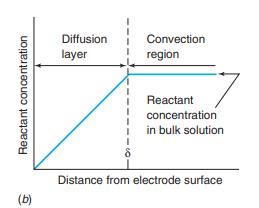
Figure 16-14b
8 = 1.61D31/6
Step by Step Solution
3.48 Rating (171 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
W is the rotation rate in radians per second We nee... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Document Format (1 attachment)
878-E-C-E-E-C (2124).docx
120 KBs Word File


