Question: Heat rejection from high-speed racing automobiles is a problem because the required heat exchangers generally create additional drag. For a car to be tested at
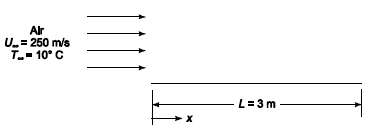
Heat rejection from high-speed racing automobiles is a problem because the required heat exchangers generally create additional drag. For a car to be tested at the Bonneville Salt Flats, it has been proposed to integrate heat rejection into the skin of the vehicle. Preliminary tests are to be performed in a wind tunnel on a flat plate without heat rejection. Atmospheric air in the tunnel is at 10?C and flows at 250 ms??1 over the 3 m long thermally non-conducting flat plate. What is the plate temperature 1 m downstream from the leading edge? How much does this temperature differ from that which exists 0.005 m from the leading edge?GIVENHigh speed air flow over a thermally non-conducting flat platePlate length (L) = 3 mAir temperature (T??) = 10?CAir speed (U??) = 250 m/sAir pressure = 1 atmosphereASSUMPTIONSSteady stateAir is on only one side of theplate
Alr U.= 250 m/s T.- 10 C L=3 m
Step by Step Solution
3.56 Rating (156 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Since the surface is nonconducting its surface temperature is equal to the adiabatic surface ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Document Format (1 attachment)
66-E-M-E-H-M-T (1677).docx
120 KBs Word File


