In the body of this chapter, disequilibrium of the following equation indicated an opportunity for a riskless
Question:
In the body of this chapter, disequilibrium of the following equation indicated an opportunity for a riskless arbitrage:
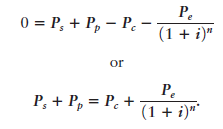
The equation was illustrated as follows. A stock sells for $105; the strike price of both the put and call is $100. The price of the put is $5, the price of the call is $20, and both options are for one year. The rate of interest is 11.1 percent, so the present value of the $100 strike price is equal to $90. Given these values, the equation holds:
0 = $105 + 5 - 20 - 90
or
$105 + 5 = $20 + 90.
The opportunity for the riskless arbitrage was then illustrated by two cases, one in which the call was overpriced ($25) and one in which the put was overpriced ($10). For each of the following sets of values, verify that a riskless arbitrage opportunity exists by determining the profit if the price of the stock rises to $110, falls to $90, or remains unchanged at $105.
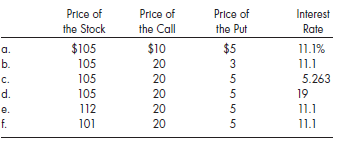
When will the opportunity for arbitrage cease, and what are the implications for the prices of each security?
Strike PriceIn finance, the strike price of an option is the fixed price at which the owner of the option can buy, or sell, the underlying security or commodity.
Step by Step Answer:






