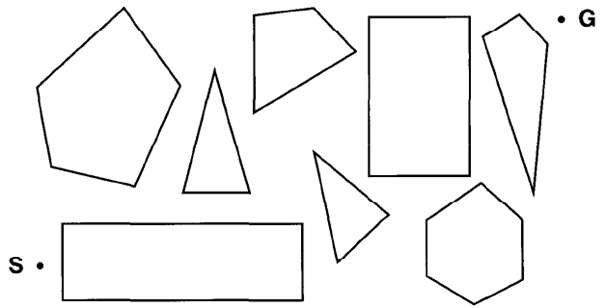
Question: In this exercise, we will examine hill climbing in the context of robot navigation, using the environment in Figure as an example. a. Repeat Exercise
In this exercise, we will examine hill climbing in the context of robot navigation, using the environment in Figure as an example.
a. Repeat Exercise 3.16 using hill climbing. Does your agent ever get stuck in a local minimum? Is it possible for it to get stuck with convex obstacles?
b. Construct a non-convex polygonal environment in which the agent gets stuck.
c. Modify the hill-climbing algorithm so that, instead of doing a depth-i search to decide where to go next, it does a depth-k search. It should find the best k-step path and do one step along it, and then repeat the process.
d. Is there some k for which the new algorithm is guaranteed to escape from localminima?
S
Step by Step Solution
3.35 Rating (164 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Hill climbing is surprisingly effective at finding reasonable i... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Document Format (1 attachment)
21-C-S-A-I (54).docx
120 KBs Word File


