Question: Marston Marble Corporation is considering a merger with the Conroy Concrete Company. Conroy is a publicly traded company, and its beta is 1.30. Conroy has
Marston Marble Corporation is considering a merger with the Conroy Concrete Company. Conroy is a publicly traded company, and its beta is 1.30. Conroy has been barely profitable, so it has paid an average of only 20% in taxes during the last several years. In addition, it uses little debt; its target ratio is just 25%, with the cost of debt 9%. If the acquisition were made, Marston would operate Conroy as a separate, wholly owned subsidiary. Marston would pay taxes on a consolidated basis, and the tax rate would therefore increase to 35%. Marston also would increase the debt capitalization in the Conroy subsidiary to wd = 40%, for a total of $22.27 million in debt by the end of Year 4, and pay 9.5% on the debt. Marston?s acquisition department estimates that Conroy, if acquired, would generate the following free cash flows and interest expenses (in millions of dollars) in Years 1-5:
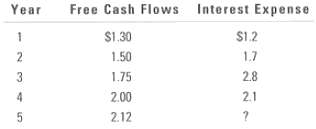
In Year 5, Conroy?s interest expense would be based on its beginning-of-year (that is, the cnd-of-Ycar-4) debt, and in subsequent years both interest expense and free cash flows are projected to grow at a rate of 6%.
These cash flows include all acquisition effects. .1arson?s cost of equity is 10.5%, its beta is 1.0, and its cost of debt is 9.5%. The risk-free rite is 6%, and the market risk premium is 4.5%.
a. What is the value of Conroy?s unlevered operations, and what is the value of Conroy?s tax shields under the proposed merger and financing arrangements?
b. What is the dollar value of Conroy?s operations? If Conroy has $10 million in debt outstanding, how much would Marston be willing to pay for Conroy?
Year Free Cash Flows Interest Expense $1.2 $1.30 1.50 1.7 2.8 3 1.75 2.1 2.00 2.12
Step by Step Solution
3.48 Rating (165 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
a The appropriate discount rate reflects the risk of the cash flows Thus it is Conroys unlevered cos... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Document Format (1 attachment)
53-B-C-F-M-A-G (23).docx
120 KBs Word File


