Stress relaxation after cessation of shear flow. A viscoelastic fluid is in steady-state flow between a pair
Question:
Stress relaxation after cessation of shear flow. A viscoelastic fluid is in steady-state flow between a pair of parallel plates, with vx = ?y If the flow is suddenly stopped (i.e., ?/becomes zero), the stresses do not go to zero as would be the case for a NewtonJan fluid. Explore this stress relaxation phenomenon using a 3-constant Oldroyd model (Eq. 8.5-3 with ?2 = ?1 = ?0 = 0).?
(a) Show that in steady-state flow to what extent does this expression agree with the experimental data in Fig. 8.2-4??
(b) By using Example 8.5-1 (part a) show that, if the flow is stopped at t = 0, the shear stress for t > 0 will be this shows why ?xx is called the "relaxation time." This relaxation of stresses after the fluid motion has stopped is characteristic of viscoelastic materials.?
(c) What is the normal stress ?xx during steady shear flow and after cessation of the flow?
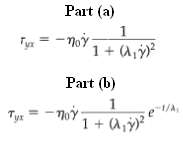
Step by Step Answer:






