Question: Modify Table 11-1 by indicating if each specific control procedure listed there is preventive (P), detective (D), or corrective (C) in nature. Table 11-1 Threats
Modify Table 11-1 by indicating if each specific control procedure listed there is preventive (P), detective (D), or corrective (C) in nature.
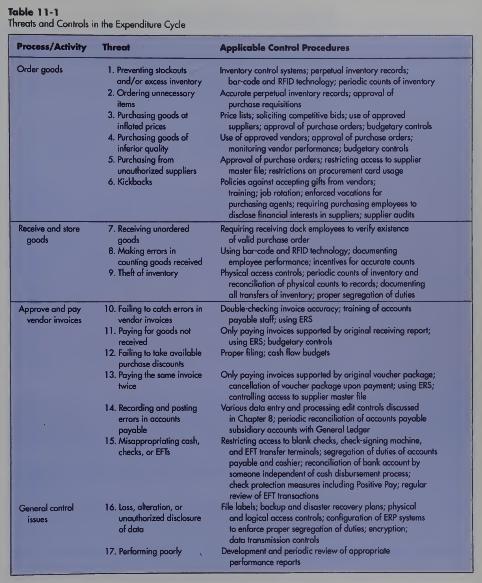
Table 11-1 Threats and Controls in the Expenditure Cycle Process/Activity Order goods Receive and store goods Approve and pay vendor invoices General control issues Threat 1. Preventing stockouts and/or excess inventory 2. Ordering unnecessary items 3. Purchasing goods at inflated prices 4. Purchasing goods of inferior quality 5. Purchasing from unauthorized suppliers 6. Kickbacks 7. Receiving unordered goods 8. Making errors in counting goods received 9. Theft of inventory 10. Failing to catch errors in vendar invoices 11. Paying for goods not received 12. Failing to take available purchase discounts 13. Paying the same invoice twice 14. Recording and posting errors in accounts payable 15. Misappropriating cash, checks, or EFT 16. Loss, aberation, or unauthorized disclosure of data 17. Performing poorly Applicable Control Procedures Inventory control systems; perpetual inventory records; bar-code and RFID technology: periodic counts of inventory Accurate perpetual inventory records; approval of purchase requisitions Price lists; soliciting competitive bids; use of approved suppliers; approval of purchase orders; budgetary controls Use of approved vendors; approval of purchase orders; monitoring vendor performance; budgetary controls Approval of purchase orders; restricting access to supplier master file; restrictions on procurement card usage Policies against accepting gifts from vendors; training; job rotation; enforced vocations for purchasing agents; requiring purchasing employees to disclose financial interests in suppliers; supplier audits Requiring receiving dock employees to verify existence of valid purchase order Using bar code and RFID technology; documenting employee performance; incentives for accurate counts Physical access controls; periodic counts of inventory and reconciliation of physical counts to records; documenting all transfers af inventory; proper segregation of duties Double-checking invoice accuracy, training of accounts payable staff; using ERS Only paying invoices supported by original receiving report; using ERS; budgetary controls Proper filing: cash flow budgets Only paying invoices supported by original voucher package; cancellation of voucher package upon payment; using ERS; controlling access to supplier master file Various data entry and processing edit controls discussed in Chapter 8; periodic reconciliation of accounts payable subsidiary accounts with General Ledger Restricting access to blank checks, check-signing machine, and EFT transfer terminals; segregation of duties of accounts payable and cashier; reconciliation of bank account by someone independent of cush disbursement process; check protection measures including Positive Pay; regular review of EFT transactions File labels; backup and disaster recovery plans; physical and logical access controls; configuration of ERP systems to enforce proper segregation of duties; encryption; data transmission controls Development and periodic review of appropriate performance reports
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


