Question: (a) Explain why the wavelet expansion (9.136) defines a linear transformation on Rn that takes a wavelet coefficient vector c = (c 0 , c
(a) Explain why the wavelet expansion (9.136) defines a linear transformation on Rn that takes a wavelet coefficient vector c = (c0, c1, . . . , cn−1)T to the corresponding sample vector f = (f0, f1, . . . , fn−1)T.
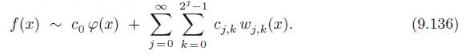
(b) According to Theorem 7.5, the wavelet map must be given by matrix multiplication f = Wn c by a 2 × 2n matrix W = Wn. Construct W2, W3 and W4.
(c) Prove that the columns of Wn are obtained as the values of the wavelet basis functions on the 2n sample intervals.
(d) Prove that the columns of Wn are orthogonal.
(e) Is Wn an orthogonal matrix? Find a formula for Wn−1.
(f) Explain why the wavelet transform is given by the linear map, c = Wn−1 f.
Theorem 7.5.
Every linear function L:Rn → Rm is given by matrix multiplication, L[v] = Av, where A is an m × n matrix.
2-1 f(x) Cop(a) + AW; (2). j=0 k=0 (9.136)
Step by Step Solution
3.48 Rating (161 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
a The wavelet expansion 9136 defines a linear transformation on Rn that takes a wavelet coefficient ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


