Question: Consider the problem of finding the shortest path between two points on a plane that has convex polygonal obstacles as shown in Figure 3.31. This
Consider the problem of finding the shortest path between two points on a plane that has convex polygonal obstacles as shown in Figure 3.31. This is an idealization of the problem that a robot has to solve to navigate in a crowded environment.
a. Suppose the state space consists of all positions (x, y) in the plane. How many states are there? How many paths are there to the goal?
b. Explain briefly why the shortest path from one polygon vertex to any other in the scene must consist of straight-line segments joining some of the vertices of the polygons. Define a good state space now. How large is this state space?
c. Define the necessary functions to implement the search problem, including an ACTIONS function that takes a vertex as input and returns a set of vectors, each of which maps the current vertex to one of the vertices that can be reached in a straight line. (Do not forget the neighbors on the same polygon.) Use the straight-line distance for the heuristic function.
d. Apply one or more of the algorithms in this chapter to solve a range of problems in the domain, and comment on their performance.
Figure 3.31
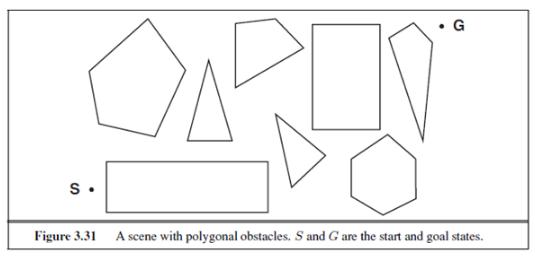
G Figure 3.31 A scene with polygonal obstacles. S and G are the start and goal states.
Step by Step Solution
3.41 Rating (167 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
a If we consider all x y points then there are an infinite number of states and of paths b For this ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


