Question: Given the example of the Viterbi algorithm processing the probabilistic finite state machine of Figure 13.7 and 13.8: Figure 13.7 Figure 13.8 a. Why
Given the example of the Viterbi algorithm processing the probabilistic finite state machine of Figure 13.7 and 13.8:
Figure 13.7
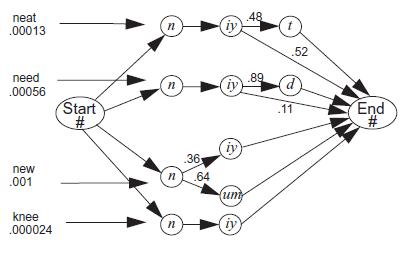
Figure 13.8
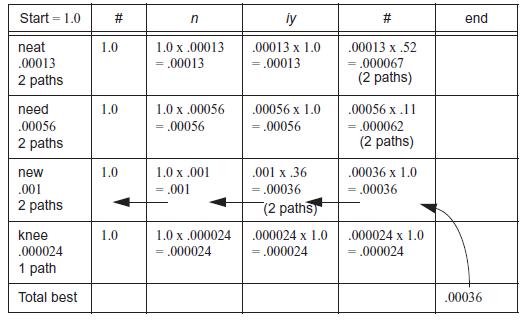
a. Why is new seen as a better interpretation than knee for the observed phones?
b. How are alternative states in the probabilistic finite state machine handled by the Viterbi algorithm, for example, the choice of the phones uw and iy in the word new?
Step by Step Solution
3.22 Rating (157 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
a In the Viterbi algorithm processing the probabilistic finite state machine new is seen as a better ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


