Question: Write a program that implements the fuzzy controller of Section 9.2.2. Data from section 9.2.2 There are two assumptions that are essential for the use
Write a program that implements the fuzzy controller of Section 9.2.2.
Data from section 9.2.2

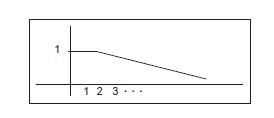
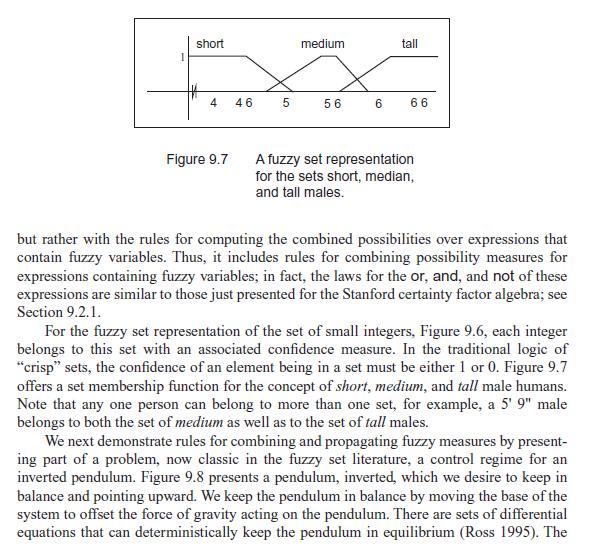
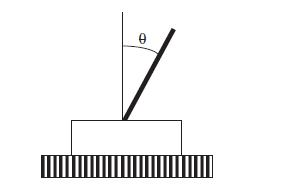
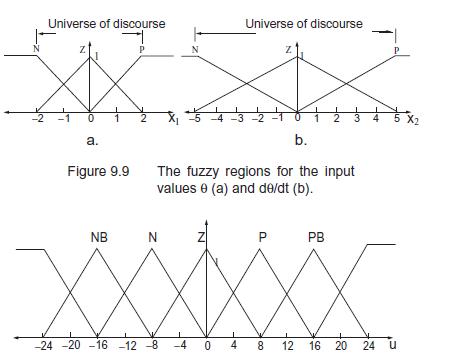

There are two assumptions that are essential for the use of formal set theory. The first is with respect to set membership: for any element and a set belonging to some universe, the element is either a member of the set or else it is a member of the complement of that set. The second assumption, referred to as the law of excluded middle, states that an element cannot belong to both a set and also to its complement. Both these assumptions are violated in Lotfi Zadeh's fuzzy set theory. In fact, the sets and reasoning laws of traditional set theory are referred to as crisp, from the fuzzy set viewpoint. Zadeh's main contention (Zadeh 1983) is that, although probability theory is appropriate for measuring randomness of information, it is inappropriate for measuring the meaning of information. Indeed, much of the confusion surrounding the use of English words and phrases is related to lack of clarity (vagueness) rather than randomness. This is a crucial point for analyzing language structures and can also be important in creating a measure of confidence in production rules. Zadeh proposes possibility theory as a measure of vagueness, just as probability theory measures randomness. Zadeh's theory expresses lack of precision in a quantitative fashion by introducing a set membership function that can take on real values between 0 and 1. This notion of a fuzzy set can be described as follows: let S be a set and s a member of that set. A fuzzy subset F of S is defined by a membership function mF(s) that measures the "degree" to which s belongs to F. A standard example of a fuzzy set, as presented in Figure 9.6, is for S to be the set of positive integers and F to be the fuzzy subset of S called small integers. Now various integer values can have a "possibility" distribution defining their "fuzzy membership" in the set of small integers: mF (1) = 1.0, mF (2) = 1.0, mF (3) = 0.9, mF(4) = 0.8, ..., mF (50) = 0.001, etc. For the statement that positive integer X is a small integer, mF creates a possibility distribution across all the positive integers (S). Fuzzy set theory is not concerned with how these possibility distributions are created,
Step by Step Solution
3.52 Rating (166 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Fuzzy Controller for Inverted Pendulum Full Implementation I Theoretical Foundation of Fuzzy Control Section 922 The inverted pendulum is a classic control problem where the objective is to balance a ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


