A Canadian longitudinal study examines whether giving antibiotics in infancy increases the likelihood that the child will
Question:
A Canadian longitudinal study examines whether giving antibiotics in infancy increases the likelihood that the child will be overweight later in life. The children were classified as having received antibiotics or not during the first year of life and then being overweight or not at 9 years old. The study included 616 children, and the results are shown in Table 2.14.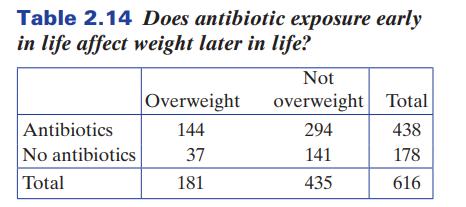
(a) What proportion of all children in the study were given antibiotics during the first year of life?
(b) What proportion of all children in the study were classified as overweight at age 9?
(c) What proportion of those receiving antibiotics were classified as overweight at age 9?
(d) What proportion of those not receiving antibiotics were classified as overweight at age 9?
(e) If we use p̂A to denote the proportion from part (c) and p̂N to denote the proportion from part (d), calculate the difference in proportion being overweight, p̂A − p̂N, between those who were exposed to antibiotics and those who weren’t.
(f) What proportion of all children classified as overweight were given antibiotics during the first year of life?
Step by Step Answer:

Statistics, Enhanced Unlocking The Power Of Data
ISBN: 9781119308843
2nd Edition
Authors: Robin H Lock, Patti Frazer Lock, Kari Lock Morgan, Eric F Lock, Dennis F Lock





