Question: Apply Stokes' Theorem to evaluate (oint_{C} mathbf{F} cdot d mathbf{r}) by finding the flux of (operatorname{curl}(mathbf{F})) across an appropriate surface. (mathbf{F}=langle 3 y,-2 x, 3
Apply Stokes' Theorem to evaluate \(\oint_{C} \mathbf{F} \cdot d \mathbf{r}\) by finding the flux of \(\operatorname{curl}(\mathbf{F})\) across an appropriate surface.
\(\mathbf{F}=\langle 3 y,-2 x, 3 yangle, \quad C\) is the circle \(x^{2}+y^{2}=9, z=2\), oriented counterclockwise as viewed from above.
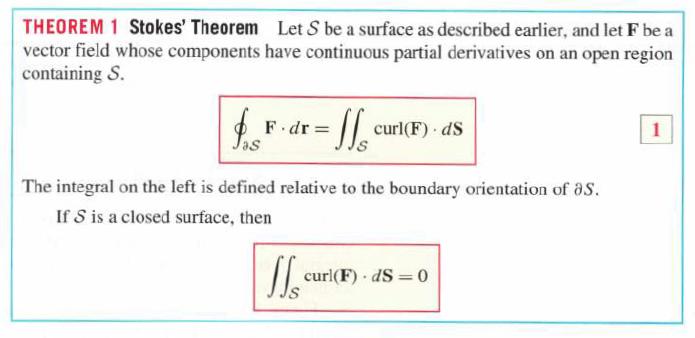
THEOREM 1 Stokes' Theorem Let S be a surface as described earlier, and let F be a vector field whose components have continuous partial derivatives on an open region containing S. $. F.dr= - J1 The integral on the left is defined relative to the boundary orientation of aS. If S is a closed surface, then If cu curl(F). dS curl(F) dS=0 . 1
Step by Step Solution
3.43 Rating (153 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Choose for the surface mathcalS the interior of the given circle and parametrize mathcalS by mathbfr... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


