Question: Let r(s) be an arc length parametrization of a closed curve C of length L. We call C an oval if d/ds > 0 (see
Let r(s) be an arc length parametrization of a closed curve C of length L. We call C an oval if dθ/ds > 0 (see Exercise 71). Observe that −N points to the outside of C. For k > 0, the curve C1 defined by r1(s) = r(s) − kN is called the expansion of c(s) in the normal direction.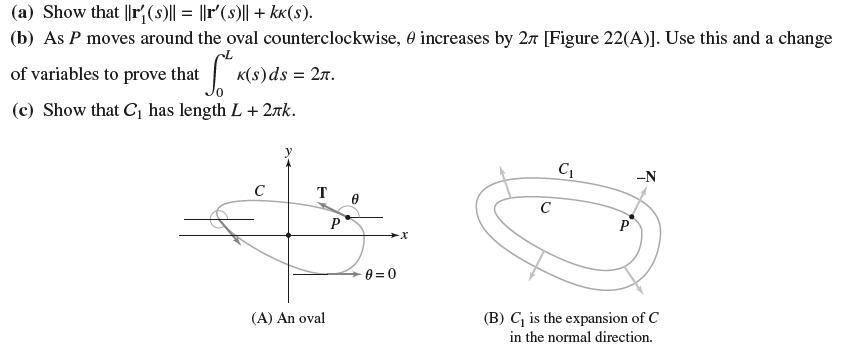
Data From Exercise 71
The angle of inclination at a point P on a plane curve is the angle θ between the unit tangent vector T and the x-axis (Figure 21). Assume that r(s) is a arc length parametrization, and let θ = θ(s) be the angle of inclination at r(s). Prove that
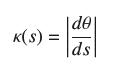
Observe that T(s) = (cos θ(s), sin θ(s)).
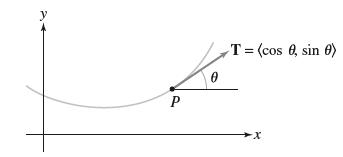
(a) Show that ||r(s)|| = ||r'(s)|| + kk(s). (b) As P moves around the oval counterclockwise, increases by 2 [Figure 22(A)]. Use this and a change at for x (c) Show that C has length L + 2k. of variables to prove that K(s) ds = 2. C T (A) An oval P 0 -0=0 C C P -N (B) C is the expansion of C in the normal direction.
Step by Step Solution
3.36 Rating (152 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


