Question: Verify Stokes' Theorem for the given vector field and surface, oriented with an upwardpointing normal. (mathbf{F}=leftlangle e^{y-z}, 0,0ightangle), the square with vertices ((1,0,1),(1,1,1),(0,1,1)), and ((0,0,1))
Verify Stokes' Theorem for the given vector field and surface, oriented with an upwardpointing normal.
\(\mathbf{F}=\left\langle e^{y-z}, 0,0ightangle\), the square with vertices \((1,0,1),(1,1,1),(0,1,1)\), and \((0,0,1)\)
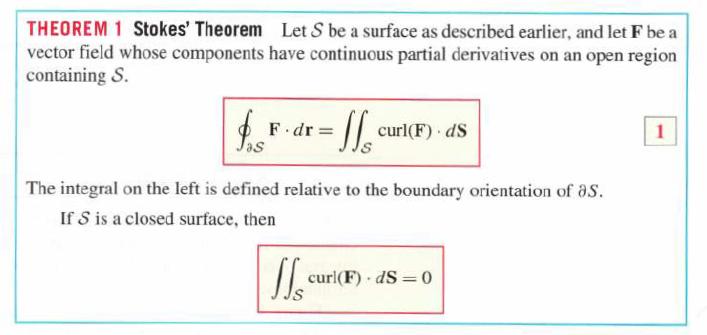
THEOREM 1 Stokes' Theorem Let S be a surface as described earlier, and let F be a vector field whose components have continuous partial derivatives on an open region containing S. as F.dr = JG Ils The integral on the left is defined relative to the boundary orientation of S. If S is a closed surface, then curl(F). ds curl(F) dS=0 1
Step by Step Solution
3.45 Rating (164 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step 1 Compute the integral around the boundary curve The boundary consists of four segments C1 C2 C3 and C4 shown in the figure We parametrize the se... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


