Question: Let g(t) = t 4 and define (x) = 1 0 e x2 dx = 1.46265 and 2 0 e x2 dx =
Let g(t) = t4 and define ƒ(x) = ∫10ex2 dx = 1.46265 and ∫20ex2 dx = 16.45263. Use this information to find
(a)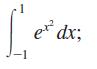
(b) Verify that ƒ′(1) = g(x). The fact that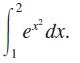
is true for all continuous functions g is an alternative version of the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus.
(c) Let us verify the result in part (b) for a function whose antiderivative cannot be found. Let g(t) = et2 and let c = 0. Use the integration feature on a graphing calculator to find ƒ(x) for x = 1 and x = 1.01. Then use the definition of the derivative with h = 0.01 to approximate ƒ′(1), and compare it with g(1).
-1 e dx;
Step by Step Solution
3.33 Rating (168 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
a gt t 4 and c 1 use substitution b Since gt t 4 t... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


