The activity of the enzyme amylase can be measured at a particular temperature by placing a sample
Question:
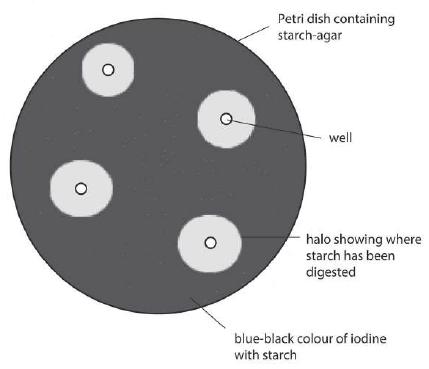
The activity of the enzyme amylase can be measured at a particular temperature by placing a sample into a Petri dish containing starch-agar (‘a starch-agar plate’). Starch-agar is a jelly containing starch. One or more ‘wells’ (small holes) are cut in the agar jelly with a cork borer, and a sample of the enzyme is placed in each well.
The enzyme molecules then diff use through the agar and gradually digest any starch in their path. At the end of the experiment, iodine in potassium iodide solution is poured over the plate. Most of the plate will turn blue black as iodine reacts with starch, but a clear ‘halo’ (circle) will be seen around the well where starch has been digested. Measuring the size of the halo can give an indication of the activity of the enzyme.
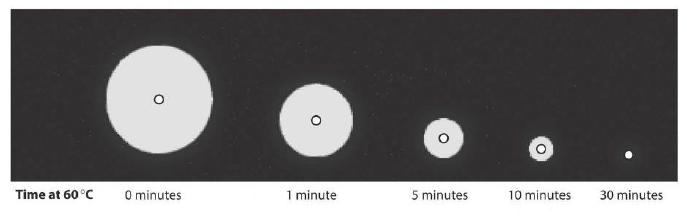
A student decided to investigate the rate at which a mammalian amylase is denatured at 60 °C. She heated diff erent samples of the enzyme in a water bath at 60 °C for 0, 1, 5, 10 and 30 minutes. She then allowed the samples to cool down to room temperature and placed samples of equal volume in the wells of five starch-agar plates, one plate for each heating period. She then incubated the plates in an oven at 40 °C for 24 hours.
The results of the student’s experiment are shown on the next page. A diagram of one dish is shown, and the real size of one halo from each dish is also shown.
a. Why did the student cut four wells in each dish rather than just one?
b. One dish contained samples from amylase which was not heated (time zero). This is a control dish. Explain the purpose of this control.
c. Explain why the starch-agar plates were incubated at 40 °C and not room temperature.
d. Describe what was happening in the dishes during the 24 hours of incubation.
e. Why was it important to add the same volume of amylase solution to each well?
f. Measure the diameter in mm of the representative halo from each dish. Record the results in a suitable table.
g. Only one halo from each dish is shown in the diagrams. In practice there was some variation in the diameters of the four halos in each dish. How would you allow for this when processing your data?
h. Plot a graph to show the eff ect of length of time at 60 °C on the activity of the enzyme.
i. Describe and explain your results.
j. Another student discovered that amylases from fungi and bacteria are more resistant to high temperatures than mammalian amylases. Using starch-agar plates as a method for measuring the activity of an amylase at 40 °C, outline an experiment that the student could perform to discover which amylase is most resistant to heat. Note that temperatures up to 120 °C can be obtained by using an autoclave (pressure cooker).
k. Enzymes are used in many industrial processes where resistance to high temperatures is an advantage. State three other variables apart from temperature which should be controlled in an industrial process involving enzymes.
Step by Step Answer:

Cambridge International AS And A Level Biology
ISBN: 9781107636828
4th Edition
Authors: Mary Jones, Richard Fosbery, Jennifer Gregory, Dennis Taylor





