Question: Methylamine, CH 3 NH 2 , is a weak base used as a building block for some pharmaceuticals. If you prepare an aqueous solution of
Methylamine, CH3NH2, is a weak base used as a building block for some pharmaceuticals. If you prepare an aqueous solution of methylamine for use in a synthesis, you might need to know its pH to avoid unwanted side reactions. Calculate the pH and percentage protonation of a 0.20 m aqueous solution of methylamine at 25°C. The Kb for CH3NH2 is 3.6 * 10–4.
ANTICIPATE Because methylamine is a weak base (like all amines), you should expect pH > 7 and only a small percentage protonation.
PLAN Proceed as in Toolbox 6D.2.
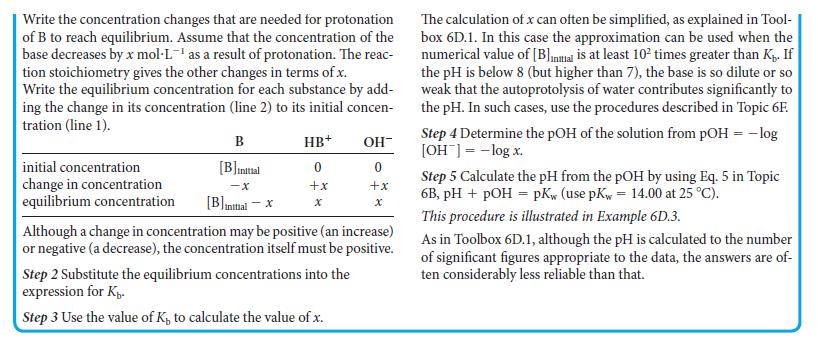
Toolbox 6D.2 HOW TO CALCULATE THE PH OF A SOLUTION OF A WEAK BASE CONCEPTUAL BASIS Proton transfer equilibrium is established as soon as a weak base is dissolved in water, and so the hydroxide ion concentration can be calculated from the initial concentration of the base and the value of its basicity constant. Because the hydroxide ions are in equilibrium with the hydronium ions, the values of pOH and pKw can be used to calculate the pH. PROCEDURE Step 1 Write the chemical equation and the expression for K for the proton transfer equilibrium. Set up a table with columns labeled by the base (B), the conjugate acid of the base (HB*), and OH. In the first row below the headings, show the initial concentration of each species. For this step, assume that no base molecules have been protonated.
Step by Step Solution
3.47 Rating (163 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step 1 Write the proton transfer equilibrium and the corresponding equilibrium table with all concen... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


