Question: Use Appendix 2D to find the values for the atomic radii of germanium and antimony, as well as the ionic radii for Ge 2+ and
Use Appendix 2D to find the values for the atomic radii of germanium and antimony, as well as the ionic radii for Ge2+ and Sb3+. What do these values suggest about the chemical properties of these two ions?
Appendix 2D 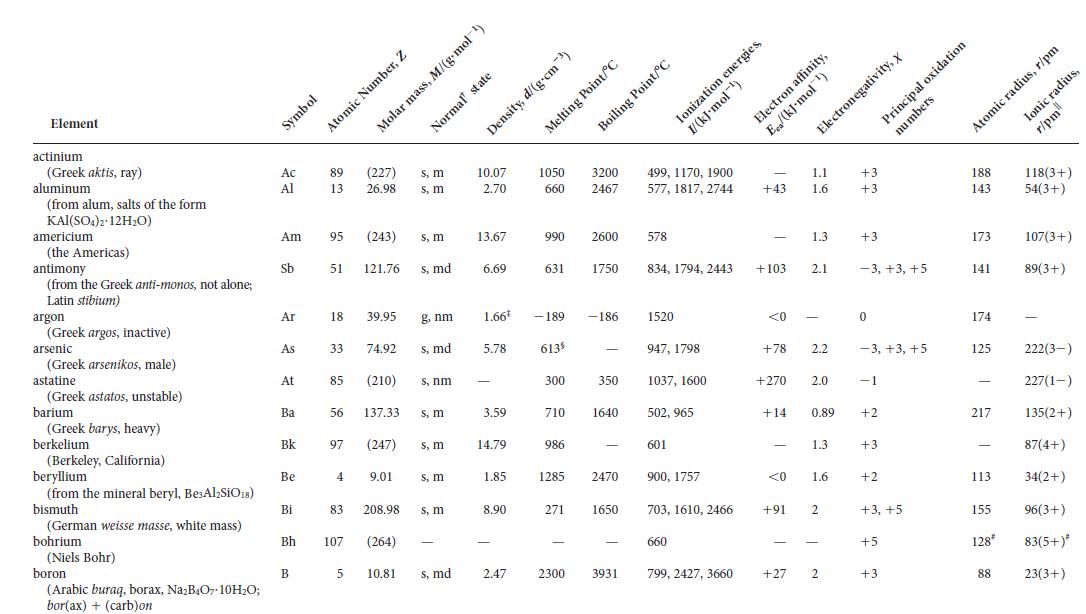
Element actinium (Greek aktis, ray) aluminum (from alum, salts of the form KAI KAI(SO4)2 12HO) americium meric (the Americas) antimony (w (from the Greek anti-monos, not alone; Latin stibium) Lati argon (Greek argos, inactive) arsenic iscine (Greek arsenikos, male) astatine Statile (Greek astatos, unstable) barium arium arram (Greek barys, heavy) berkelium (Berkeley, California) beryllium (from the mineral beryl, Be Al-SiO18) bismuth (German weisse masse, white mass) bohrium (Niels Bohr) boron (Arabic buraq, borax, NaB4O7-10HO; bor(ax) + (carb)on Symbol Ac Al Am Sb Ar As At Ba Bk Be Bi Bh 89 (227) 13 26.98 95 (243) 51 121.76 18 39.95 56 Atomic Number, Z 97 85 (210) 4 83 107 33 74.92 s, md B 5 Molar 137.33 (247) 9.01 s, m s, m 208.98 (264) s, m s, md g, nm s, nm s, m s, m s, m s, m 10.81 s, md mass, M/(g-mol-) Normal' state 10.07 2.70 13.67 6.69 1.66 5.78 3.59 14.79 1.85 8.90 2.47 1050 3200 660 2467 631 990 2600 - 189 613 300 710 986 1285 Density, d/(g.cm) Melting Point/C 271 2300 Boiling Point/C 1750 -186 350 1640 2470 1650 3931 499, 1170, 1900 577, 1817, 2744 578 Ionization energies, I/(kJ-mol-) 834, 1794, 2443 1520 947, 1798 1037, 1600 502, 965 601 900, 1757 703, 1610, 2466 660 799, 2427, 3660 Electron affinity, 1.1 +43 1.6
Step by Step Solution
3.41 Rating (151 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
From Appendix 2D the radii in picometers are Ge 123 Ge 90 S... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


