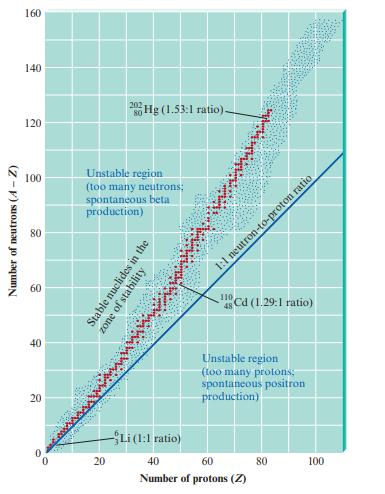
Fig. 18.1 illustrates the zone of stability. What is the zone of stability? Stable light nuclides have
Question:
Fig. 18.1 illustrates the zone of stability. What is the zone of stability? Stable light nuclides have about equal numbers of neutrons and protons. What happens to the neutron-to-proton ratio for stable nuclides as the number of protons increases? Nuclides that are not already in the zone of stability undergo radioactive processes to get to the zone of stability. If a nuclide has too many neutrons, which process(es) can the nuclide undergo to become more stable? Answer the same question for a nuclide having too many protons.
Fig. 18.1
Fantastic news! We've Found the answer you've been seeking!
Step by Step Answer:
Related Book For 

Chemistry An Atoms First Approach
ISBN: 9781305079243
2nd Edition
Authors: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Question Posted:





