A cycloalkane is a hydrocarbon that contains a ring of carbon atoms with two hydrogen atoms bonded
Question:
A cycloalkane is a hydrocarbon that contains a ring of carbon atoms with two hydrogen atoms bonded to each carbon. Th e standard enthalpy changes for the combustion of several gaseous cycloalkanes to form gaseous water and carbon dioxide have been measured and are summarized in the table below.![]()
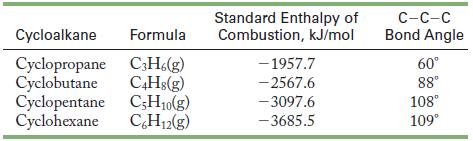
Because all reactants and products are in the gaseous state, bond energies may be used to estimate the enthalpy changes for these reactions.
(a) The formulas of the related noncyclic alkanes are C3H8, C4H10, C5H12, and C6H14. What are the oxidation numbers of the carbon atoms in the cycloalkane and noncyclic alkanes? Can you explain the trend?
(b) Draw Lewis structures of the four cycloalkanes. According to VSEPR, what should the bond angles be?
(c) Combine the measured enthalpies of combustion with the bond energies for C=O, O-H, O2, and C-H to calculate the average bond energy of the C-C bond in each of these cycloalkanes.
(d) The general formula for the cycloalkanes is (CH2)n.
Determine the value of n for each cycloalkane in the table, and determine the amount of energy given off per CH2 unit for each compound. What trend do you see?
(e) Compare the observed angles given in the table with those found in part b and offer an explanation for the trend in the C-C bond energies calculated in part c.
Step by Step Answer:

Chemistry Principles And Practice
ISBN: 9780534420123
3rd Edition
Authors: Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball





