Question: This exercise studies the impact of aggressive techniques to exploit instruction-level parallelism in the processor when used in the design of shared-memory multiprocessor systems. Consider
a. Following the convention of Figure 5.11, let us divide the execution time into instruction execution, cache access, memory access, and other stalls. How would you expect each of these components to differ between system A and system B?
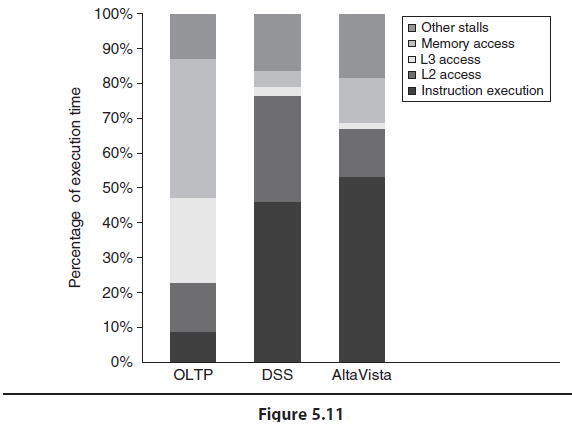
b. Based on the discussion of the behavior of the On-Line Transaction Processing (OLTP) workload in Section 5.3, what is the important difference between the OLTP workload and other benchmarks that limits benefit from a more aggressive processor design?
100% - O Other stalls O Memory access O L3 access I L2 access I Instruction execution 90% 80% - 70% - 60% 50% - 40% - 30% - 20% - 10% - 0% OLTP DSS AltaVista Figure 5.11 Percentage of execution time
Step by Step Solution
3.28 Rating (172 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
a The instruction execution component would be significantly sped up because the outoforder executio... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


