Question: In Problem 24, Chapter 11, we discussed an EVAD, a device that works in parallel with the human heart to help pump blood in patients
In Problem 24, Chapter 11, we discussed an EVAD, a device that works in parallel with the human heart to help pump blood in patients with cardiac conditions. The device has a transfer function
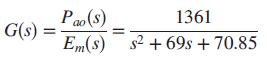
where Em(s) is the motor’s armature voltage, and Pao(s) is the aortic blood pressure (Tasch, 1990). Using continuous techniques, a cascaded compensator is designed in a unity feedback configuration with a transfer function
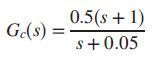
Selecting to control the device using a microcontroller, a discrete equivalent has to be found for Gc(s). Do the following:
a. Find an appropriate sampling frequency for the discretization.
b. Translate the continuous compensator into a discrete compensator using the sampling frequency found in Part a.
c. Use Simulink to simulate the continuous and discrete systems on the same graph for a unit step input. There should be little difference between the compensated continuous and discrete systems.
Data from Problem 24 Chapter 11:
An electric ventricular assist device (EVAD) that helps pump blood concurrently to a defective natural heart in sick patients can be shown to have a transfer function
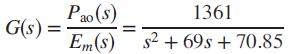
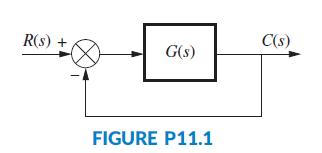
The input, Em(s), is the motor’s armature voltage, and the output is Pao(s), the aortic blood pressure (Tasch, 1990). The EVAD will be controlled in the closed-loop configuration shown in Figure P11.1.
Pao(s) 1361 G(s) : %3D Em(s) s2 + 69s +70.85
Step by Step Solution
3.45 Rating (171 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


