Question: Packet information flow in a router working under TCP/IP can be modeled using the linearized transfer function where C = link capacity (packets/second) N =
Packet information flow in a router working under TCP/IP can be modeled using the linearized transfer function
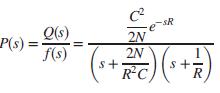
where
C = link capacity (packets/second)
N = load factor (number of TCP sessions)
Q= expected queue length
R = round trip time (second)
p =probability of a packet drop
The objective of an active queue management (AQM) algorithm is to automatically choose a packet-drop probability, p, so that the queue length is maintained at a desired level. This system can be represented by the block diagram of Figure P7.13 with the plant model in the P(s) block, the AQM algorithm in the G(s) block, and F(s) = H(s) = 1. Several AQM algorithms are available, but one that has received special attention in the literature is the random early detection (RED) algorithm. This algorithm can be approximated with G(s) = LK/s + K, where L and K are constants (Hollot, 2001). Find the value of L required to obtain a 10% steady-state error for a unit step input when C= 3750 packets/s, N=50 TCP sessions, R= 0.1 s, and K= 0.005.
Q(s) -SR 2N P(s) = f(s) 2N R-C s+ R
Step by Step Solution
3.28 Rating (160 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


