Question: Here is another realization of the fast exponentiation algorithm. Demonstrate that it is equivalent to the one in Figure 9.8. 1. (mathrm{f} leftarrow 1 ;
Here is another realization of the fast exponentiation algorithm. Demonstrate that it is equivalent to the one in Figure 9.8.
1. \(\mathrm{f} \leftarrow 1 ; \mathrm{T} \leftarrow \mathrm{a} ; \mathrm{E} \leftarrow \mathrm{b}\)
2. if odd(e) then \(\mathrm{f} \leftarrow \mathrm{f} \times \mathrm{T}\)
3. \(\mathrm{E} \leftarrow[\mathrm{E} / 2]\)
4. \(\mathrm{T} \leftarrow \mathrm{T} \times \mathrm{T}\)
5. if \(\mathrm{E}>0\) then goto 2
6. output \(f\)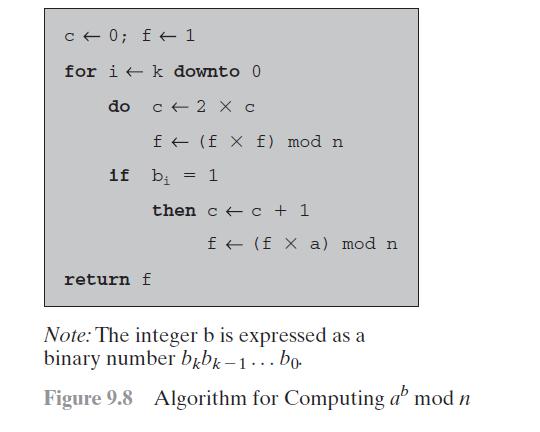
c 0; f 1 for ik downto 0 do c 2 X c f (f x f) mod n if b = 1 then cc + 1 return f f (f X a) mod n Note: The integer b is expressed as a binary number bkbk-1... bo Figure 9.8 Algorithm for Computing a mod n
Step by Step Solution
3.49 Rating (152 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
First let us consider the algorithm in Figure 98 The binary representation of b b is read from lef... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


