Question: Consider the crack problem shown for the anti-plane strain case with u = v = 0, w = w(x,y). From Section 7.4, the governing equation
Consider the crack problem shown for the anti-plane strain case with u = v = 0, w = w(x,y). From Section 7.4, the governing equation for the unknown displacement component with zero body force was given by Laplace’s equation, which in polar coordinates reads.
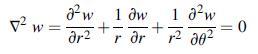
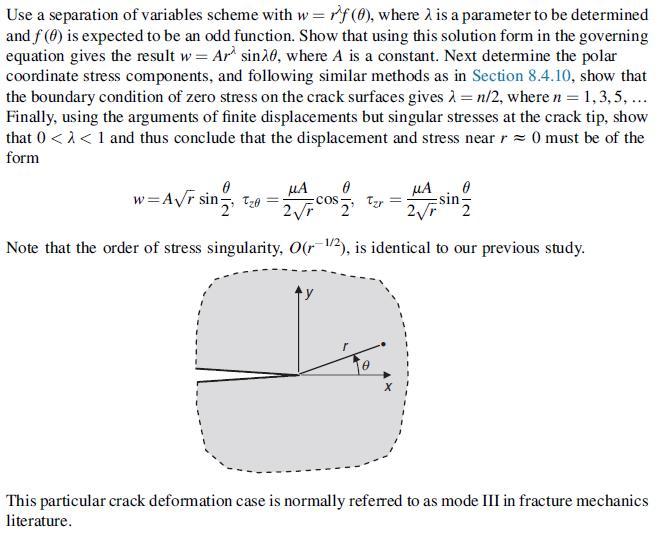
Data from section 8.4.10
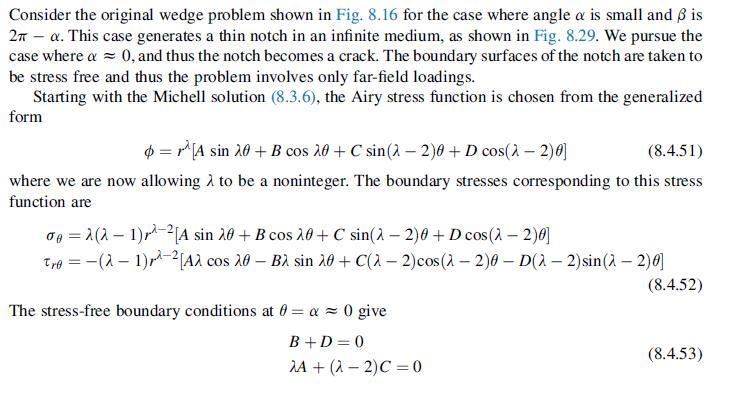
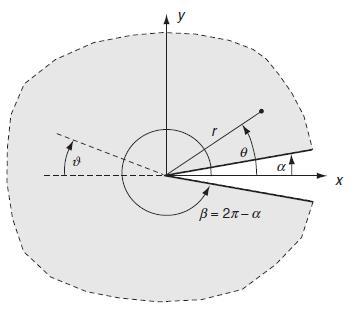
![while the identical conditions at 0=6=27- = 2 produce sin 2 (2 2) ^ 2 si - sin 272C +[cos 2(2-2) - cos 2] =](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1706/2/0/6/88965b2a6a9bb63f1706206888536.jpg)



Data from section 7.4
D 10w + = + 2 20 r r aw 1 dw dr2 0
Step by Step Solution
★★★★★
3.50 Rating (160 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock

Using w Ar f0 in Vw0 KKDr Wr hr 0 fK 0 f Solution f Asin 20 B cos 20 Cho... View full answer

Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


