Question: Modify example 9.2 by assuming there is only one firm. Assume that both and 1 = can take two values: L ,
Modify example 9.2 by assuming there is only one firm. Assume that both η and ν1=ν can take two values: νL, νH, and ηL, ηH. Denote pLL=Pr(η=ηL, ν=νL) as the probablity that both parameters take their low values, and similarly define pLH, pHL, and pHH. Define abatement costs by C(l)=c·l2/2 and damages by D(A)=δ⋅A2/2, where A=η(emax−νl) is the ambient pollution level.
(a) Calculate the optimal level for abatement input and the optimal ambient emission tax rate.
(b) Consider the following special cases and interpret: (i) pLH=pHL=0, (ii) pLL=pHH=0, and (iii) Pr(η
,ν)=Pr(η)×Pr(ν)=pη•pν.
Example 9.2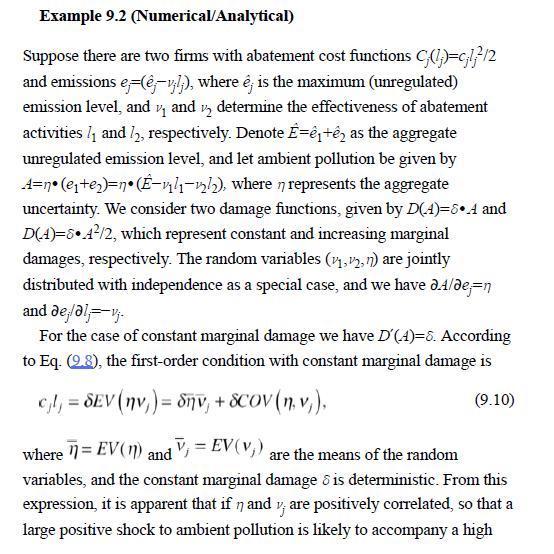

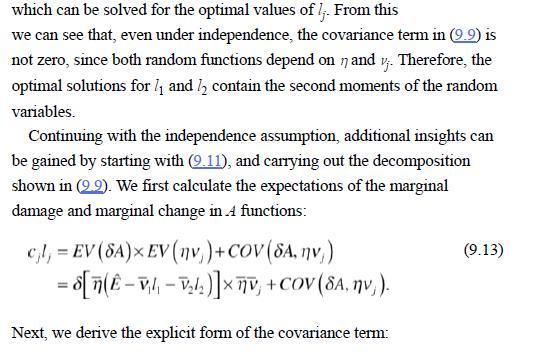


Example 9.2 (Numerical/Analytical) Suppose there are two firms with abatement cost functions C(1)=cl/2 and emissions e-(e-vlj), where e; is the maximum (unregulated) emission level, and and determine the effectiveness of abatement 1/1 activities 1 and 12, respectively. Denote E=+ as the aggregate unregulated emission level, and let ambient pollution be given by A=n (e+)=n (E-v-22), where n represents the aggregate uncertainty. We consider two damage functions, given by D(4)=8.4 and D(4)=84/2, which represent constant and increasing marginal damages, respectively. The random variables (,2,n) are jointly distributed with independence as a special case, and we have d./de-n and defalvj. For the case of constant marginal damage we have D'(A)=8. According to Eq. (9.8), the first-order condition with constant marginal damage is cl = SEV (nv) = nv, +SCOV (n. v), (9.10) where = EV (1) and V = EV(v) are the means of the random variables, and the constant marginal damage is deterministic. From this expression, it is apparent that if n and v; are positively correlated, so that a large positive shock to ambient pollution is likely to accompany a high
Step by Step Solution
3.36 Rating (152 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Based on the information provided and the modification of Example 92 to a single firm scenario we would approach the problem in two stages first by se... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


