A brand synonymous with private villas, tropical garden spas, and retail galleries promoting traditional craft, Banyan Tree
Question:
A brand synonymous with private villas, tropical garden spas, and retail galleries promoting traditional craft, Banyan Tree Hotels & Resorts received its first guest in 1994 in Phuket, Thailand, and has since grown into a leading manager and developer of niche and premium resorts, hotels, and spas in the Asia-Pacific region.
Despite having minimal advertising, Banyan Tree achieved a global exposure and a high level of brand awareness through the company’s public relations and global marketing programs. Much interest was also generated by the company’s socially responsible business values and practices caring for the social and natural environments. With a firm foothold in the medium-sized luxury resorts market, the company introduced a new and contemporary brand, Angsana, in 2000 to gain a wider customer base.
As the resorts market became increasingly crowded with similar competitive offerings, lured by the success of Banyan Tree, the company had to contemplate expanding its business and preserving its distinct identity. Banyan Tree and Angsana resorts were expanding geographically outside of Asia and also into the urban hotel market in major cities throughout the world.
With around 30 hotels and resorts scheduled to open over the next three years, Banyan Tree faced the challenge of translating and maintaining the success of a niche Asian hospitality brand into various market segments on a global scale.
COMPANY BACKGROUND
By October 2015, Banyan Tree Holdings Ltd. (BTHR) managed or had ownership interests in 38 resorts and hotels, 67 spas, 79 retail galleries, and 2 golf courses in 28 countries. Since its Tree, had won some 1,200 international tourism, hospitality, design, and marketing awards, which included “2014 Forbes Travel Guide Award,” “Top 10 Hotels In Mexico” in 2014 by US News for Banyan Tree Mayakoba, “Best Spa Resort in China” in 2014 for Banyan Tree Lijiang from the 7th Annual TTG China Travel Awards, “National Geographic Traveler”
award for Banyan Tree Yangshuo in 2014, and “Best Spa Operator” at the 25th Annual TTG Travel Awards 2014 (for the 10th consecutive year) for Banyan Tree Spa.
BTHR was founded by Ho Kwon Ping, a travel enthusiast and former journalist, and his wife Claire Chiang, a strong advocate of corporate social responsibility. Prior to entering the hotel and resort business, Ho spent some 15 years managing the family business, which was involved in everything imaginable, such as commodities, food products, consumer electronics, and property development. It competed mainly on cost and was not dominant in any particular country or industry. Meanwhile, Chiang was deeply involved in sociology and social issues.
The closing of a factory in Thailand one year after its opening—because it lost out to other low-cost producers in Indonesia—was the last straw for Ho, who then realized that a low-cost strategy was not only difficult to follow but would also lead nowhere. Determined to craft something proprietary that would allow the company to become a price maker rather than a price taker, Ho decided that building a strong brand was the only way for him to maintain a sustainable competitive advantage.
The idea of entering the luxury resorts market was inspired by the gap in the hotel industry that giant chains such as the Hilton and Shangri-La could not fill. There was a market segment that wanted private and intimate accommodation but without the expectation of glitzy chain hotels. This was fueled by the sharp price gap between the luxurious Aman Resorts and other resorts in the luxury resorts market. For example, in 2004, the Amanpuri in Thailand, one of Aman’s resorts, charged a rack rate for its villas ranging from $650 to over $7,000 a night, whereas the prices of other luxury resorts, such as the Shangri-La Hotel and Phuket Arcadia Beach Resort by Hilton in Thailand were priced below $350.
Noticing the big difference in prices between Aman Resorts and the other resorts in the luxury resorts market, Ho saw potential for offering an innovative niche product that could also bridge the price gap in this market. Ho and Chiang had backpacked throughout the world in their youth and were seasoned travelers themselves. Their extensive travel experience is evident in their non-conforming beliefs that resorts should provide more than just accommodation. Ho and Chiang hit upon the idea of building a resort comprising individual villas with locally inspired architectural design and positioned as a romantic and intimate escapade for guests. Banyan Tree moved its positioning into the higher end of the luxury market, and by 2015, its rack rates for its basic category were typically between $600 and $1,200 for the resort in Phuket, and between €600 and € 3,500 for the resort in the Seychelles.
Operations at Banyan Tree began with only one resort in Phuket, situated on a former mining site once deemed too severely ravaged to sustain any form of development by a United Nations Development Program planning unit and the Tourism Authority of Thailand. It was a bold decision, but the company, together with Ho, Chiang, and Ho’s brother Ho Kwon Cjan, restored it after extensive rehabilitation works costing a total of $250 million. The Banyan Tree Phuket was so successful when it was finally launched that the company worked quickly to build two other resorts, one at Bintan Island in Indonesia and the other at Vabbinfaru Island in the Maldives. The company has never looked back since. Even though Asia’s travel industry experienced periodic meltdowns such as the Asian economic crisis in 1997–8, the September 11 attacks on the World Trade Center in 2001, the dot.com crisis in 2001–2, the SARS outbreak in 2003, the Indian Ocean tsunami on December 26, 2004, the World Economic Crisis in 2008–9, and the Euro Crisis from 2011 through to 2015, no employee was retrenched; instead, Banyan Tree grew its number of resorts and rooms aggressively, and its room rates rose steadily.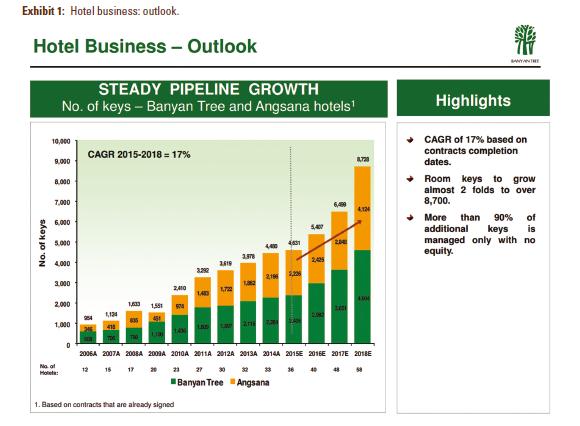
STUDY QUESTIONS
1. What are the main factors that contributed to Banyan Tree’s success?
2. Evaluate Banyan Tree’s brand positioning and communication strategies. Can Banyan Tree maintain its unique positioning in an increasingly overcrowded resorts market?
3. Discuss whether the brand portfolio of Banyan Tree, Angsana, and Cassia, as well as the product portfolio of beach resorts, services residences, city hotels, spas, galleries, and museum shops fit as a family. What are your recommendations to Banyan Tree for managing these brands and products in the future?
4. What effect does the practice of corporate social responsibility have on brand equity?
5. What potential problems do you foresee bringing Banyan Tree to the Americas, Europe, and the Middle East? How could Banyan Tree address those issues?
Step by Step Answer:






