Question: Verify that y 1 = x and y 2 = x 2 are linearly independent solutions on the entire real line of the equation x
Verify that y1 = x and y2 = x2 are linearly independent solutions on the entire real line of the equation
x2y'' - 2xy' + 2y = 0,
but that W(x , x2) vanishes at x = 0. Why do these observations not contradict part (b) of Theorem 3?
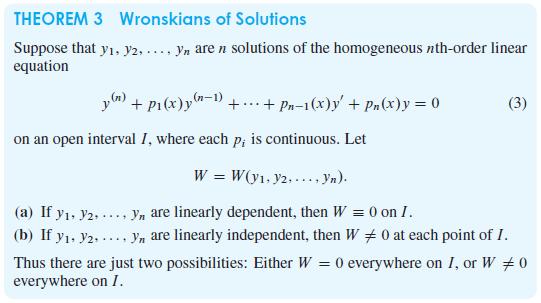
THEOREM 3 Wronskians of Solutions Suppose that y, y2, ..., yn are n solutions of the homogeneous nth-order linear equation y() + P(x) y(n-1)+...+ Pn-1(x)y' + Pn(x) y = 0 on an open interval I, where each p, is continuous. Let (a) If y, 2, (b) If y. Y2.. **** (3) W = W(y, y2...., yn). yn are linearly dependent, then W = 0 on I. yn are linearly independent, then W #0 at each point of I. Thus there are just two possibilities: Either W = 0 everywhere on I, or W #0 everywhere on I.
Step by Step Solution
3.36 Rating (152 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
When the equati... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


