Question: Using the par curve from Example 2, Example 4, and Example 5, the yield-to-maturity for a one-year annual coupon bond is 2%, for a two-year
Using the par curve from Example 2, Example 4, and Example 5, the yield-to-maturity for a one-year annual coupon bond is 2%, for a two-year annual coupon bond is 3%, and for a three-year annual coupon bond is 4%. We know that if we generate the paths in the tree correctly and discount the cash flows directly, the three-year, 5% annual coupon bond should still be priced at 102.8105, as calculated in Example 5.
There are four paths through the three-year tree. We discount the cash flows along each of the four paths and take their average, as shown in Exhibits 28, 29, and 30.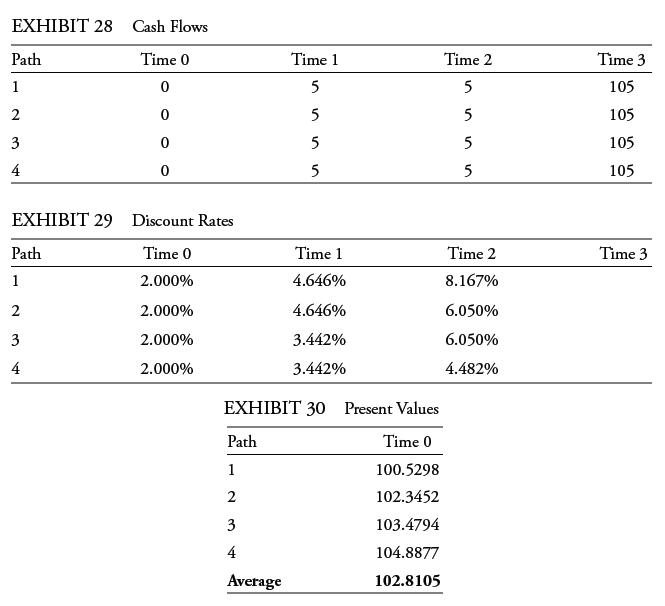
EXHIBIT 28 Cash Flows Time 0 0 0 0 0 Path 1 2 3 4 EXHIBIT 29 Discount Rates Time 0 2.000% 2.000% 2.000% 2.000% Path 1 2 3 4 Path 1 2 3 4 Time 1 5 5 5 5 EXHIBIT 30 Present Values Time 0 100.5298 102.3452 103.4794 104.8877 102.8105 Average Time 1 4.646% 4.646% 3.442% 3.442% Time 2 5 5 5 5 Time 2 8.167% 6.050% 6.050% 4.482% Time 3 105 105 105 105 Time 3
Step by Step Solution
3.50 Rating (153 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
The present values are calculated by discounting the cash flows in Exhibit ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


