A porous water vapor barrier is placed over the tissue implant shown in the figure in the
Question:
a. Making use of the Fuller€”Schettler€”Giddings correlation in the calculations, what is the effective diffusion coefficient (DAe) of H2O vapor in the randomly micro porous water vapor barrier?
b. What is the thickness of the vapor barrier (L) required to limit the rate of water evaporation from the tissue to 0.180 g H2O/cm2 · day? State all assumptions for your analysis.
c. What is the concentration of dissolved oxygen in the tissue (CBL *, gmole O2/L tissue) at the interface between the tissue and the porous vapor barrier (z = 0)?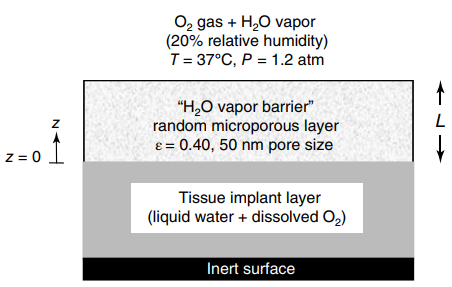
Fantastic news! We've Found the answer you've been seeking!
Step by Step Answer:
Related Book For 

Fundamentals Of Momentum Heat And Mass Transfer
ISBN: 9781118947463
6th Edition
Authors: James Welty, Gregory L. Rorrer, David G. Foster
Question Posted:





