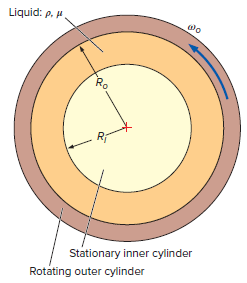
A rotating viscometer consists of two concentric cylindersa stationary inner cylinder of radius R i and an
Question:
Fantastic news! We've Found the answer you've been seeking!
Step by Step Answer:
Related Book For 

Fundamentals of Thermal-Fluid Sciences
ISBN: 978-0078027680
5th edition
Authors: Yunus A. Cengel, Robert H. Turner, John M. Cimbala
Question Posted:





